Effect of Polymer Composition on the Optical Properties of a New Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorophore: A Combined Experimental and Computational Approach
- PMID: 37688156
- PMCID: PMC10489943
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15173530
Effect of Polymer Composition on the Optical Properties of a New Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorophore: A Combined Experimental and Computational Approach
Abstract
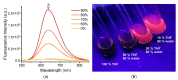
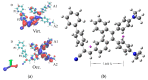
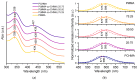
Nowadays, fluorophores with a tetraphenylethylene (TPE) core are considered interesting due to the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) behavior that enables their effective use in polymer films. We propose a novel TPE fluorophore (TPE-BPAN) bearing two dimethylamino push and a 4-biphenylacetonitrile pull moieties with the typical AIE characteristics in solution and in the solid state, as rationalized by DFT calculations. Five different host polymer matrices with different polarity have been selected: two homopolymers of poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) and poly(cyclohexyl methacrylate) (PCHMA) and three copolymers at different compositions (P(MMA-co-CHMA) 75:25, 50:50, and 25:75 mol%). The less polar comonomer of CHMA appeared to enhance TPE-BPAN emission with the highest quantum yield (QY) of about 40% measured in P(MMA-co-CHMA) 75:25. Further reduction in polymer polarity lowered QY and decreased the film stability and adhesion to the glass surface. LSC performances were not significantly affected by the matrix's polarity and resulted in around one-third of the state-of-the-art due to the reduced QY of TPE-BPAN. The theoretical investigation based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations clarified the origin of the observed AIE and the role played by the environment in modulating the photophysical behavior.
Keywords: aggregation-induced emission; density functional theory investigations; luminescent solar concentrator; methacrylate copolymers; optical and device efficiencies; push–pull tetraphenylethylene fluorophore; quantum yield (TPE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Laveyne J.I., Bozalakov D., Van Eetvelde G., Vandevelde L. Impact of Solar Panel Orientation on the Integration of Solar Energy in Low-Voltage Distribution Grids. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2020;2020:2412780. doi: 10.1155/2020/2412780. - DOI
-
- Richards B.S., Howard I.A. Luminescent Solar Concentrators for Building Integrated Photovoltaics: Opportunities and Challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023;16:3214–3239. doi: 10.1039/D3EE00331K. - DOI
-
- Pucci A. Luminescent Solar Concentrators Based on Aggregation Induced Emission. Isr. J. Chem. 2018;58:837–844. doi: 10.1002/ijch.201800028. - DOI
-
- Hu R., Qin A., Tang B.Z. AIE Polymers: Synthesis and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020;100:101176. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2019.101176. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

