Fabrication of High-Performance Natural Rubber Composites with Enhanced Filler-Rubber Interactions by Stearic Acid-Modified Diatomaceous Earth and Carbon Nanotubes for Mechanical and Energy Harvesting Applications
- PMID: 37688238
- PMCID: PMC10490170
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15173612
Fabrication of High-Performance Natural Rubber Composites with Enhanced Filler-Rubber Interactions by Stearic Acid-Modified Diatomaceous Earth and Carbon Nanotubes for Mechanical and Energy Harvesting Applications
Abstract
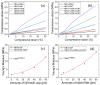
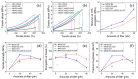
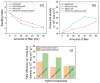
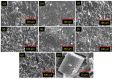
Mechanical robustness and high energy efficiency of composite materials are immensely important in modern stretchable, self-powered electronic devices. However, the availability of these materials and their toxicities are challenging factors. This paper presents the mechanical and energy-harvesting performances of low-cost natural rubber composites made of stearic acid-modified diatomaceous earth (mDE) and carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The obtained mechanical properties were significantly better than those of unfilled rubber. Compared to pristine diatomaceous earth, mDE has higher reinforcing efficiencies in terms of mechanical properties because of the effective chemical surface modification by stearic acid and enhanced filler-rubber interactions. The addition of a small amount of CNT as a component in the hybrid filler systems not only improves the mechanical properties but also improves the electrical properties of the rubber composites and has electromechanical sensitivity. For example, the fracture toughness of unfilled rubber (9.74 MJ/m3) can be enhanced by approximately 484% in a composite (56.86 MJ/m3) with 40 phr (per hundred grams of rubber) hybrid filler, whereas the composite showed electrical conductivity. At a similar mechanical load, the energy-harvesting efficiency of the composite containing 57 phr mDE and 3 phr CNT hybrid filler was nearly double that of the only 3 phr CNT-containing composite. The higher energy-harvesting efficiency of the mDE-filled conductive composites may be due to their increased dielectric behaviour. Because of their bio-based materials, rubber composites made by mDE can be considered eco-friendly composites for mechanical and energy harvesting applications and suitable electronic health monitoring devices.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; diatomaceous earth; electrical properties; energy harvesting; mechanical properties; rubber nanocomposites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Thomas S., Maria H.J., editors. Progress in Rubber Nanocomposites. Woodhead Publishing; Cambridge, UK: 2017.
-
- Shahapurkar K., Gelaw M., Tirth V., Soudagar M.E.M., Shahapurkar P., Mujtaba M.A., MC K., Ahmed G.M.S. Comprehensive Review on Polymer Composites as Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Materials. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2022;30:09673911221102127. doi: 10.1177/09673911221102127. - DOI
-
- Zhan Y., Oliviero M., Wang J., Sorrentino A., Buonocore G.G., Sorrentino L., Lavorgna M., Xia H., Iannace S. Enhancing the EMI Shielding of Natural Rubber-Based Supercritical CO2 Foams by Exploiting Their Porous Morphology and CNT Segregated Networks. Nanoscale. 2019;11:1011–1020. doi: 10.1039/C8NR07351A. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Fan C., Ma Y., Zhao H., Sui J., Liu J., Sun C. Elastic Composites Fabricating for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Based on MWCNTs and Fe3O4 Unique Distribution in Immiscible NR/NBR Blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022;62:2019–2030. doi: 10.1002/pen.25985. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

