Expert Agreement on the Presence and Spatial Localization of Melanocytic Features in Dermoscopy
- PMID: 37689267
- PMCID: PMC11498320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.01.045
Expert Agreement on the Presence and Spatial Localization of Melanocytic Features in Dermoscopy
Abstract
Dermoscopy aids in melanoma detection; however, agreement on dermoscopic features, including those of high clinical relevance, remains poor. In this study, we attempted to evaluate agreement among experts on exemplar images not only for the presence of melanocytic-specific features but also for spatial localization. This was a cross-sectional, multicenter, observational study. Dermoscopy images exhibiting at least 1 of 31 melanocytic-specific features were submitted by 25 world experts as exemplars. Using a web-based platform that allows for image markup of specific contrast-defined regions (superpixels), 20 expert readers annotated 248 dermoscopic images in collections of 62 images. Each collection was reviewed by five independent readers. A total of 4,507 feature observations were performed. Good-to-excellent agreement was found for 14 of 31 features (45.2%), with eight achieving excellent agreement (Gwet's AC >0.75) and seven of them being melanoma-specific features. These features were peppering/granularity (0.91), shiny white streaks (0.89), typical pigment network (0.83), blotch irregular (0.82), negative network (0.81), irregular globules (0.78), dotted vessels (0.77), and blue-whitish veil (0.76). By utilizing an exemplar dataset, a good-to-excellent agreement was found for 14 features that have previously been shown useful in discriminating nevi from melanoma. All images are public (www.isic-archive.com) and can be used for education, scientific communication, and machine learning experiments.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
VR is an expert consultant to Inhabit Brands. NCFC is currently an employee of Microsoft and previously an employee of IBM during the conduct of a portion of the work. He has diverse investments in the healthcare and technology sectors. HK received speaker fees from Fotofinder, Eli Lilly, and Novartis and has equipment with Heine, Fotofinder, 3-Gen, and Casio. JM is a cofounder of Athena Tech s.l. HSR is a consultant for 3-Gen, Metaoptima, Dermasensor, Casio, and Caliber ID. HPS is a shareholder of MoleMap NZ and e-derm Consult GmbH and undertakes regular teledermatological reporting for both companies. He is a medical consultant for Canfield Scientific, MoleMap Australia Pty, and Blaze Bioscience and a medical advisor for First Derm. AAM received an honorarium for lecturing on the subject of dermoscopy from DermLite, Canfield, Heine, and FotoFinder. The remaining authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

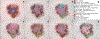
References
-
- Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk A. SLIC superpixels. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/149300?ln=en; 2010. (accessed November 22, 2023).
-
- Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2012;34:2274–82. - PubMed
-
- Argenziano G, Soyer HP. Dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions–a valuable tool for early diagnosis of melanoma. Lancet Oncol 2001;2:443–9. - PubMed
-
- Argenziano G, Soyer HP, Chimenti S, Talamini R, Corona R, Sera F, et al. Dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions: results of a consensus meeting via the Internet. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003;48:679–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

