Fumarate hydratase (FH) and cancer: a paradigm of oncometabolism
- PMID: 37689804
- PMCID: PMC10645937
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02412-w
Fumarate hydratase (FH) and cancer: a paradigm of oncometabolism
Abstract
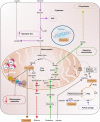
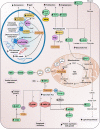
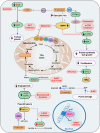
Fumarate hydratase (FH) is an enzyme of the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle whose mutations lead to hereditary and sporadic forms of cancer. Although more than twenty years have passed since its discovery as the leading cause of the cancer syndrome Hereditary leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Carcinoma (HLRCC), it is still unclear how the loss of FH causes cancer in a tissue-specific manner and with such aggressive behaviour. It has been shown that FH loss, via the accumulation of FH substrate fumarate, activates a series of oncogenic cascades whose contribution to transformation is still under investigation. In this review, we will summarise these recent findings in an integrated fashion and put forward the case that understanding the biology of FH and how its mutations promote transformation will be vital to establish novel paradigms of oncometabolism.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Weinberg RA. How cancer arises. Sci Am. 1996;275:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. - PubMed
-
- Warburg O. The metabolism of carcinoma cells. J Cancer Res. 1925;9:148–63.
-
- Freud E. Zur diagnose des carcinoms. Wien Med Blätter. 1885;9:268–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

