Astrocyte biomarkers GFAP and YKL-40 mediate early Alzheimer's disease progression
- PMID: 37690071
- PMCID: PMC10917053
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13450
Astrocyte biomarkers GFAP and YKL-40 mediate early Alzheimer's disease progression
Abstract
Introduction: We studied how biomarkers of reactive astrogliosis mediate the pathogenic cascade in the earliest Alzheimer's disease (AD) stages.
Methods: We performed path analysis on data from 384 cognitively unimpaired individuals from the ALzheimer and FAmilies (ALFA)+ study using structural equation modeling to quantify the relationships between biomarkers of reactive astrogliosis and the AD pathological cascade.
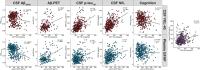
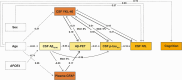
Results: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid beta (Aβ)42/40 was associated with Aβ aggregation on positron emission tomography (PET) and with CSF p-tau181 , which was in turn directly associated with CSF neurofilament light (NfL). Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) mediated the relationship between CSF Aβ42/40 and Aβ-PET, and CSF YKL-40 partly explained the association between Aβ-PET, p-tau181 , and NfL.
Discussion: Our results suggest that reactive astrogliosis, as indicated by different fluid biomarkers, influences the pathogenic cascade during the preclinical stage of AD. While plasma GFAP mediates the early association between soluble and insoluble Aβ, CSF YKL-40 mediates the latter association between Aβ and downstream Aβ-induced tau pathology and tau-induced neuronal injury.
Highlights: Lower CSF Aβ42/40 was directly linked to higher plasma GFAP concentrations. Plasma GFAP partially explained the relationship between soluble Aβ and insoluble Aβ. CSF YKL-40 mediated Aβ-induced tau phosphorylation and tau-induced neuronal injury.
Keywords: AD cascade; astrogliosis; biomarkers; chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40); glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP); preclinical Alzheimer's disease; structural equation modeling.
© 2023 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
W.P., M.S., A.B.S., C.M., K.F., A.G.E., N.J.A. have nothing to disclose. J.L.M. is currently a full‑time employee of H. Lundbeck A/S and previously served as a consultant or on advisory boards for the following for‑profit companies or has given lectures in symposia sponsored by the following for‑profit companies: Roche Diagnostics, Genentech, Novartis, Lundbeck, Oryzon, Biogen, Lilly, Janssen, Green Valley, MSD, Eisai, Alector, BioCross, GE Healthcare, and ProMIS Neurosciences. G.K. is a full‑time employee of Roche Diagnostics GmbH. M.C. is a full‑time employee of Roche Diagnostics International Ltd. and an owner of shares in Roche. H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures at symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a cofounder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. K.B. has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu. Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a cofounder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. M.S.C. has served as a consultant and at advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics International Ltd. and has given lectures at symposia sponsored by Roche Diagnostics, S.L.U. and Roche Farma, S.A. J.D.G. receives research funding from Roche Diagnostics and GE Healthcare and has given lectures at symposia sponsored by Biogen and Philips. G.S.‐B. has served as a consultant for Roche Farma, S.A. O.G.R. receives research funding from F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd. and has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Roche Diagnostics, S.L.U. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

