Unusually isolated Staphylococcus arlettae in intra-oral sutures - Case series
- PMID: 37691839
- PMCID: PMC10484312
- DOI: 10.1099/acmi.0.000555.v4
Unusually isolated Staphylococcus arlettae in intra-oral sutures - Case series
Abstract
Introduction: The human oral cavity comprises various niches such as teeth, gingiva, tongue, soft and hard palate, and various dental prostheses, all inhabited by different bacterial species. Although more than 600 taxa belong to the oral cavity, identifying Staphylococcus arlettae , an incompletely understood bacterium, has been rare.
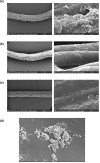
Methods: Three patients who underwent periodontal flap surgeries were reported with the incidental finding of S. arlettae associated with the intra-oral sutures placed. Environmental sampling was performed, to establish the exact source of this bacterium.
Results: Staphylococcus arlettae was isolated in three patients' intra-oral sutures. All environmental samples were negative for the presence of the bacterium.
Conclusion: . To this date, no studies have identified such an occurrence of Staphylococcus arlettae with intra-oral sutures. Its identification in association with foreign materials, such as sutures, can be considered a potential for surgical site infections and requires further investigation.
Keywords: Staphylococcus arlettae; intra-oral sutures; periodontal; scanning electron microscopy; surgical site infection.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biofilms in the edentulous oral cavity.J Prosthodont. 2008 Jul;17(5):348-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2008.00301.x. J Prosthodont. 2008. PMID: 18355168
-
Bacteriophage immobilized graphene electrodes for impedimetric sensing of bacteria (Staphylococcus arlettae).Anal Biochem. 2016 Jul 15;505:18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Anal Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27114042
-
Influence of inoculation of arsenic-resistant Staphylococcus arlettae on growth and arsenic uptake in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. Var. R-46.J Hazard Mater. 2013 Nov 15;262:1039-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.019. Epub 2012 Aug 17. J Hazard Mater. 2013. PMID: 22939092
-
Oral Microbiome as a Tool of Systemic Disease on Cleft Patients: A New Landscape.Cureus. 2023 Feb 25;15(2):e35444. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35444. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36994247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Characteristics, diagnosis and treatment of the most common bacterial diseases of the oral cavity].Orv Hetil. 2019 May;160(19):739-746. doi: 10.1556/650.2019.31377. Orv Hetil. 2019. PMID: 31055960 Review. Hungarian.
References
-
- Schleifer KH, Kilpper-Bälz R, Devriese LA. Staphylococcus arlettae sp. nov., S. equorum sp. nov. and S. k1oosii sp. nov.: three new coagulase-negative, novobiocin-resistant species from animals. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1984;5:501–509. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(84)80007-7. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
