A CT-based radiomics integrated model for discriminating pulmonary cryptococcosis granuloma from lung adenocarcinoma-a diagnostic test
- PMID: 37691867
- PMCID: PMC10483083
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-389
A CT-based radiomics integrated model for discriminating pulmonary cryptococcosis granuloma from lung adenocarcinoma-a diagnostic test
Abstract
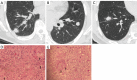
Background: Chest computed tomography (CT) is a critical tool in the diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis as approximately 30% of normal immunity individuals may not exhibit any significant symptoms or laboratory findings. Pulmonary cryptococcosis granuloma and lung adenocarcinoma can appear similar on noncontrast chest CT. This study evaluates the use of an integrated model that was developed based on radiomic features combined with demographic and radiological features to differentiate pulmonary cryptococcosis nodules from lung adenocarcinomas.
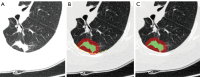
Methods: Preoperative chest CT images for 215 patients with solid pulmonary nodules with histopathologically confirmed lung adenocarcinoma and cryptococcosis infection were collected from two clinical centers (108 cases in the training set and 107 cases in the test set divided by the different hospitals). Radiomics models were constructed based on nodular lesion volume (LV), 5-mm extended lesion volume (ELV), and perilesion volume (PLV). A demoradiological model was constructed using logistic regression based on demographic information (age, sex) and 12 radiological features (location, number, shape and specific imaging signs). Both models were used to build an integrated model, the performance of which was assessed using the test set. A junior and a senior radiologist evaluated the nodules. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was conducted, and areas under the curve (AUCs), sensitivity (SEN), and specificity (SPE) of the models were calculated and compared.
Results: Among the radiomics models, AUCs of the LV, ELV, and PLV were 0.558, 0.757, and 0.470, respectively. Age, lesion number, and lobular sign were identified as independent discriminative features providing an AUC of 0.77 in the demoradiological model (SEN 0.815, SPE 0.642). The integrated model achieved the highest AUC of 0.801 (SEN 0.759, SPE 0.755), which was significantly higher than that obtained by a junior radiologist (AUC =0.689, P=0.024) but showed no significant difference from that of the senior radiologist (AUC =0.784, P=0.388).
Conclusions: An integrated model with radiomics and demoradiological features improves discrimination of cryptococcosis granulomas from solid adenocarcinomas on noncontrast CT. This model may be an effective strategy for machine complementation to discrimination by radiologists, and whole-lung automated recognition methods might dominate in the future.
Keywords: Radiomics; computed tomography (CT); lung adenocarcinoma; pulmonary cryptococcosis granuloma.
2023 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-389/coif). AW has done some consulting work for Noah Medical, Ambu, and Medtronic, and receives payment or honoraria for speaker bureaus for Biodesix, and also done some medicolegal work in the area of lung nodules. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
