Predictors of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease and prognosis in Chinese patients with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis
- PMID: 37691917
- PMCID: PMC10483132
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1209282
Predictors of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease and prognosis in Chinese patients with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis
Abstract
Background: Rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD) is the most serious complication of anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis (anti-MDA5+ DM). This study was performed to assess the prognostic factors of patients with anti-MDA5+ DM and the clinical characteristics and predictors of anti-MDA5+ DM in combination with RP-ILD.
Methods: In total, 73 MDA5+ DM patients were enrolled in this study from March 2017 to December 2021. They were divided into survival and non-survival subgroups and non-RP-ILD and RP-ILD subgroups.
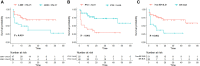
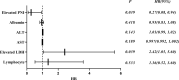
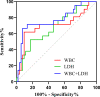
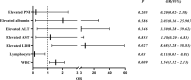
Results: The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) concentration and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) were independent prognostic factors in patients with anti-MDA5+ DM: the elevated LDH was associated with increased mortality (p = 0.01), whereas the elevated PNI was associated with reduced mortality (p < 0.001). The elevated LDH was independent risk prognostic factor for patients with anti-MDA5+ DM (HR 2.42, 95% CI: 1.02-4.83, p = 0.039), and the elevated PNI was independent protective prognostic factor (HR, 0.27; 95% CI, 0.08 - 0.94; p = 0.039). Patients who had anti-MDA5+ DM with RP-ILD had a significantly higher white blood cell count and LDH concentration than those without RP-ILD (p = 0.007 and p = 0.019, respectively). In contrast, PNI was significantly lower in patients with RP-ILD than those without RP-ILD (p < 0.001). The white blood cell count and elevated LDH were independent and significant risk factors for RP-ILD (OR 1.54, 95% CI: 1.12 - 2.13, p = 0.009 and OR 8.68, 95% CI: 1.28 - 58.83, p = 0.027, respectively), whereas the lymphocyte was an independent protective factor (OR, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01 - 0.81; p = 0.03).
Conclusion: The elevated LDH and elevated PNI were independent prognostic factors for patients with anti-MDA5+ DM. The elevated LDH was independent risk factor for RP-ILD. Patients with anti-MDA5+ DM could benefit from the measurement of LDH and PNI, which are inexpensive and simple parameters that could be used for diagnosis as well as prediction of the extent of lung involvement and prognosis.
Keywords: anti-melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody; dermatomyositis; lactate dehydrogenase; prognosis; rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Zhao, Liu, Zhao, Li, Ma and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different Multivariable Risk Factors for Rapid Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease in Anti-MDA5 Positive Dermatomyositis and Anti-Synthetase Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 7;13:845988. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845988. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35320936 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serum B-cell activator factor levels predict rapid progressive interstitial lung disease in anti-melanoma differentiation associated protein 5 antibody positive dermatomyositis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Apr 19;19(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03153-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38637830 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of characteristics and anti-MDA5 antibody distribution and effect between clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and classic dermatomyositis: a retrospective case-control study.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 27;14:1237209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1237209. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38098481 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody positive dermatomyositis associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17534666241294000. doi: 10.1177/17534666241294000. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024. PMID: 39480695 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical spectrum and therapeutics in Canadian patients with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5)-positive dermatomyositis: a case-based review.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Nov;39(11):1971-1981. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04398-2. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 31375890 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictors of relapse of polymyositis/dermatomyositis associated interstitial lung disease.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Jul 30;16(7):4229-4237. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1736. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 39144313 Free PMC article.
-
One-year mortality risk prediction model for patients with interstitial lung disease and lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):1786-1803. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2025-235. Epub 2025 May 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40535074 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Anti-MDA5 Antibody Associated Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease (RP-ILD): A Case Series.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2024 Dec 31;35(4):668-679. doi: 10.31138/mjr.020324.cco. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39886293 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying two pathways to poor prognosis in patients with anti-MDA5 antibodies: insights from prognostic factor and cytokines analysis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 Apr 16;27(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03558-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40241163 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum level of IL-6 predicts poor prognosis in anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Oct 28;26(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03415-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39468670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu L, You H, Wang L, Lv C, Yuan F, Li J, et al. Identification of three different phenotypes in anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis patients: implications for rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease prediction. Arthritis Rheumatol (2022) 75(4):609–619. doi: 10.1002/art.42308 - DOI - PubMed
-
- So J, So H, Wong VT, Ho R, Wu TY, Wong PC, et al. Predictors of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease and mortality in patients with autoantibodies against melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 dermatomyositis. Rheumatol (Oxford) (2022) 61(11):4437–44. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac094 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

