Complete genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter johnsonii, co-producing NDM-1, OXA-58, and PER-1 in a patient source
- PMID: 37692162
- PMCID: PMC10486904
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1227063
Complete genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter johnsonii, co-producing NDM-1, OXA-58, and PER-1 in a patient source
Abstract
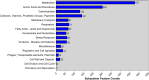
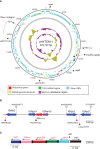
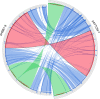
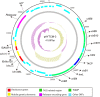
The emergence of carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter spp. has been widely reported and become a global threat. However, carbapenem-resistant A. johnsonii strains are relatively rare and without comprehensive genetic structure analysis, especially for isolates collected from human specimen. Here, one A. johnsonii AYTCM strain, co-producing NDM-1, OXA-58, and PER-1 enzymes, was isolated from sputum in China in 2018. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed that it was resistant to meropenem, imipenem, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, and cefoperazone/sulbactam. Whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatic analysis revealed that it possessed 11 plasmids. bla OXA-58 and bla PER-1 genes were located in the pAYTCM-1 plasmid. Especially, a complex class 1 integron consisted of a 5' conserved segment (5' CS) and 3' CS, which was found to carry sul1, arr-3, qnrVC6, and bla PER-1 cassettes. Moreover, the bla NDM-1 gene was located in 41,087 conjugative plasmids and was quite stable even after 70 passages under antibiotics-free conditions. In addition, six prophage regions were identified. Tracking of closely related plasmids in the public database showed that pAYTCM-1 was similar to pXBB1-9, pOXA23_010062, pOXA58_010030, and pAcsw19-2 plasmids, which were collected from the strains of sewage in China. Concerning the pAYTCM-3 plasmids, results showed that strains were collected from different sources and their hosts were isolated from various countries, such as China, USA, Japan, Brazil, and Mexico, suggesting that a wide spread occurred all over the world. In conclusion, early surveillance is warranted to avoid the extensive spread of this high-risk clone in the healthcare setting.
Keywords: Acinetobacter johnsonii; NDM-1; OXA-58; PER-1; carbapenem resistance; integron.
Copyright © 2023 Tian, Song, Ren, Huang, Wang, Fu, Zhao, Bai, Fan, Ma and Ying.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

