5-Methoxyisatin N(4)-Pyrrolidinyl Thiosemicarbazone (MeOIstPyrd) Restores Mutant p53 and Inhibits the Growth of Skin Cancer Cells, In Vitro
- PMID: 37692215
- PMCID: PMC10483675
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03824
5-Methoxyisatin N(4)-Pyrrolidinyl Thiosemicarbazone (MeOIstPyrd) Restores Mutant p53 and Inhibits the Growth of Skin Cancer Cells, In Vitro
Abstract
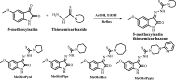
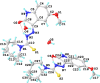
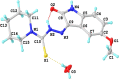
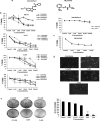
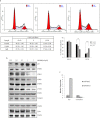
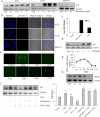
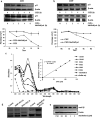
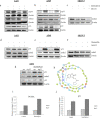
A series of novel thiosemicarbazone derivatives containing 5-methoxy isatin were designed and synthesized with modification on N(4) position. Derivatives considering structure-activity relationship have been designed and synthesized by condensing thiosemicarbazide with 5-methoxy isatin. The synthesized compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR spectroscopy, UV-visible spectroscopy, NMR (1H, 13C) spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and a single-crystal study. Biological evaluation of the synthesized compounds revealed that MeOIstPyrd is the most promising compound against skin cancer cell line, A431, with an IC50 value of 0.9 μM. In addition, MeOIstPyrd also exhibited low toxicity against the normal human fibroblast and the human embryonic kidney 293 cell line, HLF-1, and HEK293, respectively. Furthermore, the mechanistic study revealed that MeOIstPyrd efficiently inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and spheroid formation by activating the mitochondrial intrinsic apoptotic pathway. MeOIstPyrd also induces DNA damage and activates p53 irrespective of the p53 status. It increases the half-life of p53 and stabilizes p53 by phosphorylating it at ser15. Moreover, MeOIstPyrd was found to bind to MDM2 in the p53 sub-pocket and, therefore, block p53-MDM2 interaction. Our result exhibited potential anticancer activity of MeOIstPyrd in the A431 cell line and its ability in restoring mutant p53, which is an interesting and promising strategy for cancer therapeutics.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Oliveira C. G.; Maia P. I. d. S.; Souza P. C.; Pavan F. R.; Leite C. Q.; Viana R. B.; Batista A. A.; Nascimento O. R.; Deflon V. M. Manganese(II) complexes with thiosemicarbazones as potential anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 132, 21–29. 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.10.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soraires Santacruz M. C.; Fabiani M.; Castro E. F.; Cavallaro L. V.; Finkielsztein L. M. Synthesis, antiviral evaluation and molecular docking studies of N4-aryl substituted/unsubstituted thiosemicarbazones derived from 1-indanones as potent anti-bovine viral diarrhea virus agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4055–4063. 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.05.056. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

