Association between PD-L1 and Ki-67 expression and clinicopathologic features in NSCLC patients
- PMID: 37692968
- PMCID: PMC10492061
Association between PD-L1 and Ki-67 expression and clinicopathologic features in NSCLC patients
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the relationship between PD-L1, Ki-67 and the association between PD-L1, Ki-67, and clinicopathologic features and laboratory parameters in the peripheral blood of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Methods: The clinical records of 213 NSCLC patients were retrospectively reviewed. The patients were divided into high or low expression groups by cut-off values of Ki-67 and PD-L1. Correlation of PD-L1 and Ki-67 expression were analyzed by linear regression analysis. The data were tested by Mann-Whitney test. Relationship of PD-L1 and Ki-67 was tested by chi-square test.
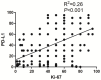
Results: Linear regression analysis revealed a positive association between the expression of PD-L1 and Ki-67 (R2=0.26, P<0.001). The clinicopathologic features and laboratory parameters such as gender, smoking history, histological types, TNM stage, tumor size, ALB, and FIB were all significantly associated with PD-L1 and Ki-67 expression (all P<0.05).
Conclusions: The expression of PD-L1 and Ki-67 is related to some clinicopathologic features and inflammatory factors, which brings new sight for exploiting combination biomarkers and therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Ki-67; Non-small cell lung cancer; PD-L1; inflammation; proliferation.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous