Intracellular chloride channel 1 and tumor
- PMID: 37693147
- PMCID: PMC10492100
Intracellular chloride channel 1 and tumor
Abstract
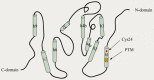
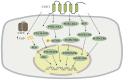
As the major intracellular anion, chloride plays an important role in maintaining intracellular and extracellular ion homeostasis, osmotic pressure, and cell volume. Intracellular chloride channel 1, which has the physiological role of forming membrane proteins in the lipid bilayer and playing ion channels, is a hot research topic in recent years. It has been found that CLIC1 does not only act as an ion channel but also participates in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and intracellular oxidation; thus, it participates in the proliferation, invasion, and migration of various tumor cells in various systems throughout the body. At the same time, CLIC1 is highly expressed in tumor cells and is associated with malignancy and a poor prognosis. This paper reviews the pathological mechanisms of CLIC1 in systemic diseases, which is important for the early diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of systemic diseases associated with CLIC1 expression.
Keywords: CLIC1; invasion; migration; proliferation; tumor.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Harrop SJ, DeMaere MZ, Fairlie WD, Reztsova T, Valenzuela SM, Mazzanti M, Tonini R, Qiu MR, Jankova L, Warton K, Bauskin AR, Wu WM, Pankhurst S, Campbell TJ, Breit SN, Curmi PM. Crystal structure of a soluble form of the intracellular chloride ion channel CLIC1 (NCC27) at 1.4-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:44993–45000. - PubMed
-
- Warton K, Tonini R, Fairlie WD, Matthews JM, Valenzuela SM, Qiu MR, Wu WM, Pankhurst S, Bauskin AR, Harrop SJ, Campbell TJ, Curmi PM, Breit SN, Mazzanti M. Recombinant CLIC1 (NCC27) assembles in lipid bilayers via a pH-dependent two-state process to form chloride ion channels with identical characteristics to those observed in Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing CLIC1. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:26003–26011. - PubMed
-
- Okada Y. Ion channels and transporters involved in cell volume regulation and sensor mechanisms. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2004;41:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Jiang L, Salao K, Li H, Rybicka JM, Yates RM, Luo XW, Shi XX, Kuffner T, Tsai VW, Husaini Y, Wu L, Brown DA, Grewal T, Brown LJ, Curmi PM, Breit SN. Intracellular chloride channel protein CLIC1 regulates macrophage function through modulation of phagosomal acidification. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:5479–5488. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jentsch TJ, Stein V, Weinreich F, Zdebik AA. Molecular structure and physiological function of chloride channels. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:503–568. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
