Super-Resolution Deep Learning Reconstruction for Improved Image Quality of Coronary CT Angiography
- PMID: 37693207
- PMCID: PMC10485715
- DOI: 10.1148/ryct.230085
Super-Resolution Deep Learning Reconstruction for Improved Image Quality of Coronary CT Angiography
Abstract
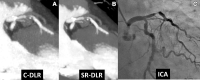
Purpose: To investigate image noise and edge sharpness of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) with super-resolution deep learning reconstruction (SR-DLR) compared with conventional DLR (C-DLR) and to evaluate agreement in stenosis grading using CCTA with that from invasive coronary angiography (ICA) as the reference standard.
Materials and methods: This retrospective study included 58 patients (mean age, 69.0 years ± 12.8 [SD]; 38 men, 20 women) who underwent CCTA using 320-row CT between April and September 2022. All images were reconstructed with two different algorithms: SR-DLR and C-DLR. Image noise, signal-to-noise ratio, edge sharpness, full width at half maximum (FWHM) of stent, and agreement in stenosis grading with that from ICA were compared. Stenosis was visually graded from 0 to 5, with 5 indicating occlusion.
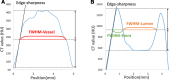
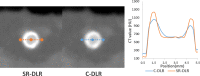
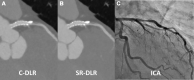
Results: SR-DLR significantly decreased image noise by 31% compared with C-DLR (12.6 HU ± 2.3 vs 18.2 HU ± 1.9; P < .001). Signal-to-noise ratio and edge sharpness were significantly improved by SR-DLR compared with C-DLR (signal-to-noise ratio, 38.7 ± 8.3 vs 26.2 ± 4.6; P < .001; edge sharpness, 560 HU/mm ± 191 vs 463 HU/mm ± 164; P < .001). The FWHM of stent was significantly thinner on SR-DLR (0.72 mm ± 0.22) than on C-DLR (1.01 mm ± 0.21; P < .001). Agreement in stenosis grading between CCTA and ICA was improved on SR-DLR compared with C-DLR (weighted κ = 0.83 vs 0.77).
Conclusion: SR-DLR improved vessel sharpness, image noise, and accuracy of coronary stenosis grading compared with the C-DLR technique.Keywords: CT Angiography, Cardiac, Coronary Arteries Supplemental material is available for this article. © RSNA, 2023.
Keywords: CT Angiography; Cardiac; Coronary Arteries.
© 2023 by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of conflicts of interest: M.T. No relevant relationships. K.K. Honoraria for lectures from Siemens Healthcare Japan, Bayer Yakuhin, and Eisai; endowed chair for Siemens Healthcare Japan and Fuji Film Medical. S.M. No relevant relationships. A.H. No relevant relationships. R.K. No relevant relationships. K. Iio No relevant relationships. K. Ichikawa No relevant relationships. D.I. No relevant relationships. H.S. No relevant relationships.
Figures
References
-
- SCOT-HEART Investigators ; Newby DE , Adamson PD , et al . Coronary CT Angiography and 5-Year Risk of Myocardial Infarction . N Engl J Med 2018. ; 379 ( 10 ): 924 – 933 . - PubMed
-
- Knuuti J , Wijns W , Saraste A , et al . 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes . Eur Heart J 2020. ; 41 ( 3 ): 407 – 477 . [Published correction appears in Eur Heart J 2020;41(44):4242.] - PubMed
-
- Miller JM , Rochitte CE , Dewey M , et al . Diagnostic performance of coronary angiography by 64-row CT . N Engl J Med 2008. ; 359 ( 22 ): 2324 – 2336 . - PubMed
-
- Budoff MJ , Dowe D , Jollis JG , et al . Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) trial . J Am Coll Cardiol 2008. ; 52 ( 21 ): 1724 – 1732 . - PubMed
-
- Meijboom WB , Meijs MF , Schuijf JD , et al . Diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography: a prospective, multicenter, multivendor study . J Am Coll Cardiol 2008. ; 52 ( 25 ): 2135 – 2144 . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

