ABDA Score: A Non-invasive Model to Identify Subjects with Fibrotic Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis in the Community
- PMID: 37693275
- PMCID: PMC10482999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.03.008
ABDA Score: A Non-invasive Model to Identify Subjects with Fibrotic Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis in the Community
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are prevalent in the community, especially among those with metabolic syndrome. Patients with fibrotic NASH are at increased risk of liver-related-events. Currently available non-invasive tests have not been utilized for screening for fibrotic NASH among the community. We aimed to develop a screening tool for fibrotic NASH among community members.
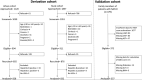
Methods: We included two large cohorts aimed at assessing cardiovascular disease among community members. Fibrotic NASH was defined using the FibroScan-aspartate aminotransferase score of ≥0.67 that identifies ≥F2 fibrosis and a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease activity score ≥4 with a specificity of 90%. Metabolic parameters, biochemical tests and anthropometry were used to develop a multivariate model.
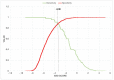
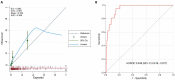
Results: The derivation cohort (n = 1660) included a population with a median age 45 years, 42.5% males, metabolic syndrome in 66% and 2.7% (n = 45) with fibrotic NASH. Multivariate analysis identified the four significant variables (Age, body mass index , Diabetes and alanine aminotransferas levels) used to derive an ABDA score. The score had high diagnostic accuracy (the area under receiver-operating characteristic curve, 0.952) with adequate internal validity. An ABDA score ≥-3.52 identified fibrotic NASH in the derivation cohort with a sensitivity and specificity of 88.9% and 88.3%. The score was validated in a second cohort (n = 357) that included 21 patients (5.9%) with fibrotic NASH, where it demonstrated a high area under receiver-operating characteristic curve (0.948), sensitivity (81%) and specificity (89.3%).
Conclusions: ABDA score utilizes four easily available parameters to identify fibrotic NASH with high accuracy in the community.
Keywords: NAFLD; diabetes; fatty liver; fibrosis; lipids.
© 2023 Indian National Association for Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Younossi Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – a global public health perspective. J Hepatol. 2019 Mar;70:531–544. - PubMed
-
- EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016 Jun;64:1388–1402. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: hepatology. Hepatology. 2018 Jan;67:328–357. Vol. XX, No. X, 2017. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

