This is a preprint.
Protein Coronas on Functionalized Nanoparticles Enable Quantitative and Precise Large-Scale Deep Plasma Proteomics
- PMID: 37693476
- PMCID: PMC10491250
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.08.28.555225
Protein Coronas on Functionalized Nanoparticles Enable Quantitative and Precise Large-Scale Deep Plasma Proteomics
Abstract
Background: The wide dynamic range of circulating proteins coupled with the diversity of proteoforms present in plasma has historically impeded comprehensive and quantitative characterization of the plasma proteome at scale. Automated nanoparticle (NP) protein corona-based proteomics workflows can efficiently compress the dynamic range of protein abundances into a mass spectrometry (MS)-accessible detection range. This enhances the depth and scalability of quantitative MS-based methods, which can elucidate the molecular mechanisms of biological processes, discover new protein biomarkers, and improve comprehensiveness of MS-based diagnostics.
Methods: Investigating multi-species spike-in experiments and a cohort, we investigated fold-change accuracy, linearity, precision, and statistical power for the using the Proteograph™ Product Suite, a deep plasma proteomics workflow, in conjunction with multiple MS instruments.
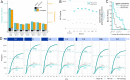
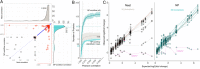
Results: We show that NP-based workflows enable accurate identification (false discovery rate of 1%) of more than 6,000 proteins from plasma (Orbitrap Astral) and, compared to a gold standard neat plasma workflow that is limited to the detection of hundreds of plasma proteins, facilitate quantification of more proteins with accurate fold-changes, high linearity, and precision. Furthermore, we demonstrate high statistical power for the discovery of biomarkers in small- and large-scale cohorts.
Conclusions: The automated NP workflow enables high-throughput, deep, and quantitative plasma proteomics investigation with sufficient power to discover new biomarker signatures with a peptide level resolution.
Keywords: LC-MS; Proteomics; clinical proteomics; cohort; nanoparticles; plasma; quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Disclosure or Potential Conflict of Interest O.C.F. has financial interest in Selecta Biosciences, Tarveda Therapeutics, and Seer where he is officer/director; and he serves as Senior Lecturer at BWH/HMS. S.F., Al.St., M.H., B.T., T.R.B., T.W., E.M.E., X.Z., E.S.O., A.A., B.L., J.C., M.F., J.W., M.G., H.X., C.S., Y.H., S.B., A.S., V.F., O.C.F., D.H. have financial interest in Seer, S.F., B.T., T.R.B., T.W., E.M.E., E.S.O., X.Z., T.W., J.C., M.F., J.W., M.G., H.X., C.S., A.S., V.F., O.C.F., D.H. have financial interest in PrognomiQ. E.D., T.A., A.H. are employed by Thermo Fisher Scientific. R.W. is a consultant to ModeRNA, Lumicell, Seer, Earli, and Accure Health. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
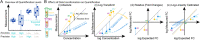



References
-
- Bollineni RC, Guldvik IJ, Grönberg H, Wiklund F, Mills IG, Thiede B. A differential protein solubility approach for the depletion of highly abundant proteins in plasma using ammonium sulfate. Analyst. 2015;140:8109–17. - PubMed
-
- Ferdosi S, Stukalov A, Hasan M, Tangeysh B, Brown TR, Wang T, et al. Enhanced Competition at the Nano–Bio Interface Enables Comprehensive Characterization of Protein Corona Dynamics and Deep Coverage of Proteomes (Adv. Mater. 44/2022). Adv Mater. 2022;34:2270307. - PubMed
-
- Donovan MKR, Huang Y, Blume JE, Wang J, Hornburg D, Mohtashemi I, et al. Peptide-centric analyses of human plasma enable increased resolution of biological insights into non-small cell lung cancer relative to protein-centric analysis. Biorxiv. 2022;2022.01.07.475393.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
