Prevalence of insulin resistance in Chinese solar greenhouse and field workers: evidence from a solar greenhouse and field workers study
- PMID: 37693717
- PMCID: PMC10485250
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1257183
Prevalence of insulin resistance in Chinese solar greenhouse and field workers: evidence from a solar greenhouse and field workers study
Abstract
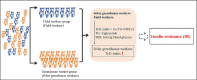
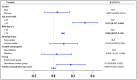
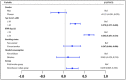
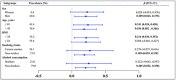
Evidence suggests that agricultural workers are at higher risk of insulin resistance (IR), but few studies have investigated IR in solar greenhouse workers, who are exposed to higher concentrations of agricultural risk factors than traditional agricultural workers. A prevalence study was conducted in a greenhouse vegetable farm in China. In total, 948 participants were enrolled in this study. Among them, 721 participants were allocated to the greenhouse worker group (G group), and 227 participants were assigned to the field worker group (F group). The TyG index, which is an indicator to evaluate prediabetes (IR), was calculated by the formula: TyG index = ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL) × fasting plasma glucose (mg/dL)/2]. To evaluate the associations of TyG index alternation with solar greenhouse and field work, multiple linear regression (MLR) and logistic regression models were performed. The TyG index in the G group (8.53 ± 0.56) was higher than that in the F group (8.44 ± 0.59) (p < 0.05). Solar greenhouse work was positively associated with an increased TyG index in both the multiple linear regression model [β = 0.207, (0.006, 0.408)] and the logistic regression model [OR = 1.469, (1.070, 2.016)]. IR was associated with the solar greenhouse work. However, the determination of agricultural hazard factors needs to be further strengthened to improve exposure assessment. Graphical Abstract.
Keywords: agriculture; field workers; insulin resistance; occupational epidemiology; prediabetes; solar greenhouse workers; triglyceride-glucose index.
Copyright © 2023 Yan, Wang, Yang, Wang, Zhou, Zhu, Ma, Tang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neurologic symptoms among solar greenhouse workers and field workers in China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Mar;30(11):31916-31922. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24412-8. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36459314
-
Chronic kidney disease among greenhouse workers and field workers in China.Chemosphere. 2022 Sep;302:134905. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134905. Epub 2022 May 10. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35561762
-
Stronger association of triglyceride glucose index than the HOMA-IR with arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes: a real-world single-centre study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Apr 22;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01274-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33888131 Free PMC article.
-
High triglyceride-glucose index is associated with subclinical cerebral small vessel disease in a healthy population: a cross-sectional study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 May 6;19(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01031-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32375783 Free PMC article.
-
Gender difference in the association between TyG index and subclinical atherosclerosis: results from the I-Lan Longitudinal Aging Study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Oct 13;20(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01391-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34645432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hortidaily Global Greenhouse News . World greenhouse vegetable statistics. (2019). Available at: https://www.hortidaily.com/article/9057219/world-greenhouse-vegetable-st...
-
- Naved Sabir BS. Protected cultivation of vegetables in global arena: a review. Indian J Agric Sci. (2013) 83:3–15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

