Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: effectiveness of salvage treatment with intratympanic dexamethasone or hyperbaric oxygen therapy in addition to systemic steroids
- PMID: 37693762
- PMCID: PMC10491011
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1225206
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: effectiveness of salvage treatment with intratympanic dexamethasone or hyperbaric oxygen therapy in addition to systemic steroids
Abstract
Background: The development of standardized treatments for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is hampered by uncertainty over the etiology of this disorder. Systemic steroids are historically the primary therapy, with variable hearing outcomes. Over the last two decades, intratympanic steroids (ITS) and hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) have been proposed as salvage treatments in case of failure of systemic steroids. The present study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of these salvage treatments in addition to systemic steroids.
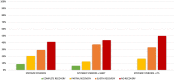
Methods: We performed a retrospective study on 75 consecutive patients with a diagnosis of ISSNHL who were admitted to the Department of Otorhinolaryngology of our hospital between December 2018 and December 2022. All patients received primary treatment with systemic steroids. In case of slight or no hearing recovery within the 5th day from the beginning of the therapy (T1), a salvage treatment with ITS or HBOT was proposed. Patients were divided into three groups according to the therapy received: systemic steroids (group A), systemic steroids + HBOT (group B), and systemic steroids + ITS (group C). Pure-tone average at 500, 1000, 2000, and 3000 Hz and the mean gain were evaluated at T1 and 3 months after the beginning of the salvage treatment (T2). The hearing recovery was assessed according to the Siegel's criteria.
Results: Sixty-two patients (31 men and 31 women, mean age 56 years) with failure of the primary treatment were definitively enrolled in the study: 34 (54.8%) in group A, 16 (25.8%) in group B, and 12 (19.4%) in group C. The ratio of patients responding to therapy was higher in group A (29.4%) than in groups B (18.75%) and C (16.7%). We did not find any statistically significant difference between groups in terms of mean hearing gain at T2 (17.4 ± 15.4 dB in group A vs. 18.6 ± 21.1 dB in group B and 15.7 ± 14.2 dB in group C, p = 0.9).
Conclusion: In our experience, ITS or HBOT associated with systemic steroids, as salvage treatment, did not show significant improvement in hearing outcomes. The evolution of ISSNHL, regardless of the treatment, remains unpredictable.
Keywords: hyperbaric oxygen therapy; intratympanic steroids; sensorineural hearing loss; steroids; sudden hearing loss.
Copyright © 2023 Mariani, Carta, Catani, Lobina, Marrosu, Corrias, Tatti and Puxeddu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Addition of intratympanic steroid or hyperbaric oxygen treatment to systemic steroid treatment in sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss treatment, and long-term results of salvage treatment.Turk J Med Sci. 2020 Feb 13;50(1):177-183. doi: 10.3906/sag-1908-122. Turk J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31865663 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Different Treatment Protocols Using Systemic and Intratympanic Steroids with and without Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Patients with Severe to Profound Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Audiol Neurootol. 2018;23(4):199-207. doi: 10.1159/000493558. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Audiol Neurootol. 2018. PMID: 30380530 Clinical Trial.
-
Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy.Laryngoscope. 2007 Jan;117(1):3-15. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000245058.11866.15. Laryngoscope. 2007. PMID: 17202923 Review.
-
The Effectiveness of Salvage Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Following Combined Steroid Therapy for Refractory Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2024 Apr;133(4):400-405. doi: 10.1177/00034894231222692. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2024. PMID: 38197374
-
The effectiveness of intratympanic steroid injection in addition to systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Am J Otolaryngol. 2023 Jul-Aug;44(4):103872. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2023.103872. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Am J Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37060782 Review.
Cited by
-
Influential publications in sudden hearing loss: a bibliometric and visual synopsis of the top 100 cited articles.Front Neurol. 2025 Jan 20;15:1494936. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1494936. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39902389 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Recovery in Patients With Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: An Observational Study.J Audiol Otol. 2025 Jul;29(3):191-196. doi: 10.7874/jao.2025.00066. Epub 2025 Jul 18. J Audiol Otol. 2025. PMID: 40739935 Free PMC article.
-
Salvage treatment strategies for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss-a comprehensive review and meta-analysis with practical recommendations.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1627892. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1627892. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40734818 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating hyperbaric oxygen therapy as an adjunct to corticosteroids in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 May 22. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09372-2. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40405024 Review.
-
Effect of the Timing of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on the Prognosis of Patients with Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 29;11(10):2670. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102670. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders . NIDCD Fact Sheet: Sudden Deafness. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; (2018).
-
- Carta F, Lussu M, Bandino F, Noto A, Peppi M, Chuchueva N, et al. . Metabolomic analysis of urine with nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a preliminary study. Auris Nasus Larynx. (2017) 44:381–89. 10.1016/j.anl.2016.10.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous