Building Blood Vessel Chips with Enhanced Physiological Relevance
- PMID: 37693798
- PMCID: PMC10489284
- DOI: 10.1002/admt.202201778
Building Blood Vessel Chips with Enhanced Physiological Relevance
Abstract
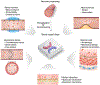
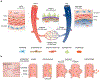
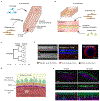
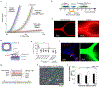
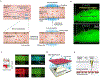
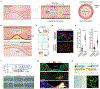
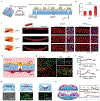
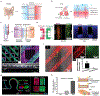
Blood vessel chips are bioengineered microdevices, consisting of biomaterials, human cells, and microstructures, which recapitulate essential vascular structure and physiology and allow a well-controlled microenvironment and spatial-temporal readouts. Blood vessel chips afford promising opportunities to understand molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying a range of vascular diseases. The physiological relevance is key to these blood vessel chips that rely on bioinspired strategies and bioengineering approaches to translate vascular physiology into artificial units. Here, we discuss several critical aspects of vascular physiology, including morphology, material composition, mechanical properties, flow dynamics, and mass transport, which provide essential guidelines and a valuable source of bioinspiration for the rational design of blood vessel chips. We also review state-of-art blood vessel chips that exhibit important physiological features of the vessel and reveal crucial insights into the biological processes and disease pathogenesis, including rare diseases, with notable implications for drug screening and clinical trials. We envision that the advances in biomaterials, biofabrication, and stem cells improve the physiological relevance of blood vessel chips, which, along with the close collaborations between clinicians and bioengineers, enable their widespread utility.
Keywords: COVID-19; angiogenesis; disease modeling; drug screening; hemodynamics; permeability; rare disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest YSZ sits on the scientific advisory board of Allevi by 3D Systems and Xellar, which however, did not participate in or bias the work.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
