Cleidocranial Dysplasia: A Rare Case Report
- PMID: 37693969
- PMCID: PMC10485440
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_212_23
Cleidocranial Dysplasia: A Rare Case Report
Abstract
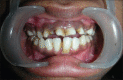
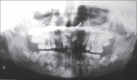
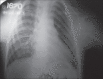
Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a rare hereditary disease of unknown etiology which was previously known as cleidocranial dysostosis. It usually follows an autosomal dominant mode of transmission with no predilection of genre or ethnic group. It is caused by a mutation of RUNX2, characterized by generalized dysplasia of the bones and teeth. Affected individuals have short stature, atypical facial features, and skeletal anomalies affecting mainly the skull and clavicle. The dental manifestations are mainly delayed exfoliation of the primary teeth and delayed eruption of the permanent teeth, with multiple impacted supernumeraries, and the absence of cellular cementum. The frequency of this disorder is 1 per million individuals. Here we report a rare case of CCD in a 23 year old female patient having most of the characteristic features of this syndrome.
Keywords: Cleidocranial dysplasia; RUNX2; dysostosis.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shafer W. G., Hine M. K., Levy B. M. Patologia bucal. Rio de Janeiro, Interamericana, 1979. 1ª. ed. Available from:https://books.google.co.in/books?id=Spk0V6TrCggC&newbks=1&newbks_redir=0... .
-
- Neville B. W., Damm D. D, Allen C. M., Bouquot JE. Patologia oral e maxilofacial. 2ª. ed Rio de Janeiro, Guanabara Koogan, 2004. Avialable from:https://www.elsevier.com/books/oral-and-maxillofacial-pathology/neville/... .
-
- Marie P., Sainton P. Sur la dysostose cleido-cranienne herediataire, Rev neurol. 6:835, 1898 On hereditary cleido-cranial dysostosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1968;58:5–7. PMID:4875295. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources