Comparative Evaluation of Extrusion of Apical Debris and Irrigant using Three Different Rotary Systems with Conventional Irrigation Methods - An In vitro Study
- PMID: 37693977
- PMCID: PMC10485542
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_210_23
Comparative Evaluation of Extrusion of Apical Debris and Irrigant using Three Different Rotary Systems with Conventional Irrigation Methods - An In vitro Study
Abstract
Aim: The present study aimed to compare and evaluate debris and irrigant extrusion from curved root canals using different rotary systems.
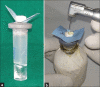
Materials and methods: 30 single-rooted mandibular canines were used in this study. The crown was decoronated, working length and initial apical diameter were established. A 1.5% agar gel model was used in this study. Samples were assigned randomly into 3 groups (n = 10 teeth per group). Protaper Next, OneShape, and Hanudent files were used according to the manufacturers' instructions for canal instrumentation. Apically extruded debris and irrigant was were computed by deducting the initial weight of the test apparatus without a tooth from its weight after the biomechanical preparation. Comparative analysis of the amount of apically extruded debris and irrigant for each of the instruments and the experimental models was performed.
Results: The statistically significant difference was found between the three experimental groups. (P < .05). Among all the groups least extrusion was observed in the Protaper Next group when used in combination with conventional irrigation.
Conclusion: All the instruments produced apically extruded debris and irrigant, but the maximum was seen with OneShape among the experimental groups.
Keywords: Apically extruded debris and irrigant; Hanudent; OneShape; ProtaperNext.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of the interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of apically extruded debris and irrigant produced by different nickel-titanium instrument systems.Braz Oral Res. 2015;29:1-6. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2015.vol29.0002. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Braz Oral Res. 2015. PMID: 25387860
-
Apically extruded debris and irrigant with two Ni-Ti systems and hand files when removing root fillings: a laboratory study.Int Endod J. 2013 Dec;46(12):1125-30. doi: 10.1111/iej.12104. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Int Endod J. 2013. PMID: 23566178
-
Comparative evaluation of apical extrusion of debris and irrigant with three rotary instruments using crown down technique - An in vitro study.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2012 May-Aug;2(2):105-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 Jun 19. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2012. PMID: 25737844 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of conventional, protaper hand and protaper rotary instrumentation system for apical extrusion of debris, irrigants and bacteria- An in vitro randomized trial.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Feb 1;9(2):e254-e258. doi: 10.4317/jced.53340. eCollection 2017 Feb. J Clin Exp Dent. 2017. PMID: 28210445 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Comparison of Apically Extruded Debris during Root Canal Preparation of Mandibular Premolars with Manual and Rotary Instruments.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2015 Summer;9(3):131-7. doi: 10.15171/joddd.2015.026. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2015. PMID: 26697144 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apical extrusion following different glide path instrumentation in curved canals of mandibular molars.Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2024 Dec;37(3):254-261. doi: 10.54589/aol.37/3/254. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2024. PMID: 40014823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mounce R. The biologic objectives of root canal therapy:Meeting the standard. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2004;25:576. - PubMed
-
- Vande Visse JE, Brilliant JD. Effect of irrigation on the production of extruded material at the root apex during instrumentation. J Endod. 1975;1:243–6. - PubMed
-
- Seltzer S, Naidorf IJ. Flare-ups in endodontics:I. Etiological factors. J Endod. 1985;11:472–8. - PubMed
-
- Kuştarci A, Akpinar KE, Er K. Apical extrusion of intracanal debris and irrigant following use of various instrumentation techniques. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105:257–62. - PubMed
-
- Kuştarci A, Akpinar KE, Sümer Z, Er K, Bek B. Apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria following use of various instrumentation techniques. Int Endod J. 2008;41:1066–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources