Bacterial Species Causing Secondary Pneumonia Infection in Pregnant Women with COVID-19
- PMID: 37694060
- PMCID: PMC10485501
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_252_23
Bacterial Species Causing Secondary Pneumonia Infection in Pregnant Women with COVID-19
Abstract
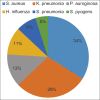
Sputum samples were taken from pregnant women infected with the COVID-19, where the study was conducted on 112 cases, and the results showed that 87 cases developed secondary bacterial infections at a rate of 78% and 25 cases were negative by 22%. The samples were cultured on solid media and incubated at 37°C. Then the samples were diagnosed by biochemical tests and using the API system. Six species of bcteria have been isolated (S. aureus, K.pneumonia P. auroginosa, H. influenza, S. pneumonia S. pyogens) by 31, 29, 12, 10, 7, and 5 isolates, respectively, where the result showed that the most common types of pneumonia were S. aureus with a percentage of 34%, followed by K. pneumonia with a percentage of 29%. The sensitivity of the isolates to eight types of common antibiotics was tested (Erythromycin, Trimethoprim, Ampicillin, Tetracycline, Augmentin, Nitrofurantoin, Meropenem, and Amikacin), where the isolates showed a high resistance to antibiotics (Erythromycin, Trimethoprim, Ampicillin), a high sensitivity of 100% to the Nitrofurantoin, and an average sensitivity to other antibiotics.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pneumonia; Secondary infection.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Protocolo de manejo clínico para o novo-coronavírus (2019-nCoV) [[Last accessed on 2020 Feb 12]]. Available from: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/manejo_clinico_covid-19_atenc... .
-
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Coronavírus: o que você precisa saber e como prevenir o contágio. [[Last accessed on 2020 Feb 18]]. Available from: https://saude.gov.br/saude-de-a-z/coronavírus .
-
- Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) [[Last accessed on 2020 Feb 25]]. Available from:https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mis... .
-
- McLuckie A, editor. Respiratory Disease and Its Management. New York: Springer; 2009. p. 51.
-
- Leach RE. 2nd. Wiley-Blackwell; 2009. Acute and Critical Care Medicine at a Glance.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources