Clinacanthus nutans L Extracts Reduce the Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, Malondialdehyde, and Interleukin-6 Levels and Improve the Langerhans Islet Area in Diabetic Rat Models
- PMID: 37694133
- PMCID: PMC10492484
- DOI: 10.1177/11795514231196462
Clinacanthus nutans L Extracts Reduce the Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, Malondialdehyde, and Interleukin-6 Levels and Improve the Langerhans Islet Area in Diabetic Rat Models
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus-induced hyperglycemia increases oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production, which play a significant role in the damage and apoptosis of pancreatic β cells. Therefore, the administration of medications that can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation plays an important role in diabetes treatment.
Objective: To probe the Clinacanthus nutans leaf extract effect on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers and the Langerhans islet area in diabetic rat models.
Design: An experimental laboratory in the animal model.
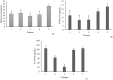
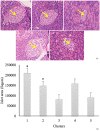
Methods: Twenty-five diabetic rat models were randomly assigned into 5 clusters. Clusters 1, 2, and 3 were administered with C. nutans leaf extract in aqueous suspension with vehicle 1% Na-CMC at 75 mg/kg body weight (BW), 150 mg/kg BW, and 300 mg/kg BW, respectively. Cluster 4 was diabetic control rats administered with metformin at a 21 mg/rat dose. Cluster 5 was a control diabetic rat only administered with 1% Na-CMC suspension. Treatment was administered orally for 14 days. On the 15th day, the rats were sacrificed to obtain blood samples and pancreatic tissues. Serum interleukin (IL)-6, malondialdehyde (MDA), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) were measured using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. Histopathological examination was performed by counting the Langerhans islet areas.
Results: The average IL-6, MDA, and TNF-α levels declined in the cluster receiving C. nutans extract and were significantly different from the untreated cluster (P < .05). Histopathological examination revealed a significant upsurge in the Langerhans islets area in diabetic rats receiving C. nutans extract at doses of 75 and 150 mg/kg (P < .05).
Conclusion: C. nutans leaf extract reduced the serum MDA, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels, and increased the Langerhans islets area in a diabetic rat model.
Keywords: Clinacanthus nutans L; Diabetes; Langerhans islet; interleukin-6; malondialdehyde; medicine; tumor necrosis factor-α.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al.. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pr. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus 2019. WHO; 2019:36.
-
- Sukarno DA, Mustika A, Rejeki PS. Effect of celery extract on fructose induced insulin resistance Rattus norvegicus. Folia Med Indones. 2020;56:269-274.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

