Bacillus subtilis NDmed, a model strain for biofilm genetic studies
- PMID: 37694162
- PMCID: PMC10485040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2023.100152
Bacillus subtilis NDmed, a model strain for biofilm genetic studies
Abstract
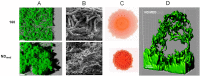
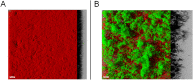
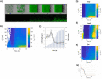
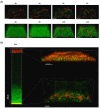
The Bacillus subtilis strain NDmed was isolated from an endoscope washer-disinfector in a medical environment. NDmed can form complex macrocolonies with highly wrinkled architectural structures on solid medium. In static liquid culture, it produces thick pellicles at the interface with air as well as remarkable highly protruding ''beanstalk-like'' submerged biofilm structures at the solid surface. Since these mucoid submerged structures are hyper-resistant to biocides, NDmed has the ability to protect pathogens embedded in mixed-species biofilms by sheltering them from the action of these agents. Additionally, this non-domesticated and highly biofilm forming strain has the propensity of being genetically manipulated. Due to all these properties, the NDmed strain becomes a valuable model for the study of B. subtilis biofilms. This review focuses on several studies performed with NDmed that have highlighted the sophisticated genetic dynamics at play during B. subtilis biofilm formation. Further studies in project using modern molecular tools of advanced technologies with this strain, will allow to deepen our knowledge on the emerging properties of multicellular bacterial life.
Keywords: Bacillus subilis; Biofilms; CLSM; Colony; NDmed; Pellicle.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Chen Y., Yan F., Chai Y., Liu H., Kolter R., Losick R., et al. Biocontrol of tomato wilt disease by Bacillus subtilis isolates from natural environments depends on conserved genes mediating biofilm formation. Environ Microbiol. 2013;15:848–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02860.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

