Effective Delivery of Vagus Nerve Stimulation Requires Many Stimulations Per Session and Many Sessions Per Week Over Many Weeks to Improve Recovery of Somatosensation
- PMID: 37694568
- PMCID: PMC10523825
- DOI: 10.1177/15459683231197412
Effective Delivery of Vagus Nerve Stimulation Requires Many Stimulations Per Session and Many Sessions Per Week Over Many Weeks to Improve Recovery of Somatosensation
Abstract
Background: Chronic sensory loss is a common and undertreated consequence of many forms of neurological injury. Emerging evidence indicates that vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) delivered during tactile rehabilitation promotes recovery of somatosensation.
Objective: Here, we characterize the amount, intensity, frequency, and duration of VNS therapy paradigms to determine the optimal dosage for VNS-dependent enhancement of recovery in a model of peripheral nerve injury (PNI).
Methods: Rats underwent transection of the medial and ulnar nerves in the forelimb, resulting in chronic sensory loss in the paw. Eight weeks after injury, rats were implanted with a VNS cuff and received tactile rehabilitation sessions consisting of repeated mechanical stimulation of the previously denervated forepaw paired with short bursts of VNS. Rats received VNS therapy in 1 of 6 systematically varied dosing schedules to identify a paradigm that balanced therapy effectiveness with a shorter regimen.
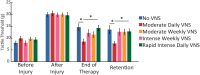
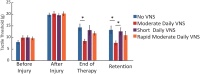
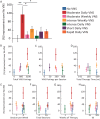
Results: Delivering 200 VNS pairings a day 4 days a week for 4 weeks produced the greatest percent improvement in somatosensory function compared to any of the 6 other groups (One Way analysis of variance at the end of therapy, F[4 70] P = .005).
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that an effective VNS therapy dosage delivers many stimulations per session, with many sessions per week, over many weeks. These results provide a framework to inform the development of VNS-based therapies for sensory restoration.
Keywords: dosage; massed training; nerve injury; neurorehabilitation; spaced training; vagal nerve stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: MPK has a financial interest in MicroTransponder, Inc., which is developing closed-loop VNS for stroke. RLR is the co-founder and CEO of XNerve, which is developing nerve stimulation therapies. The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

