SETD2 Deficiency Confers Sensitivity to Dual Inhibition of DNA Methylation and PARP in Kidney Cancer
- PMID: 37695044
- PMCID: PMC10843145
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0401
SETD2 Deficiency Confers Sensitivity to Dual Inhibition of DNA Methylation and PARP in Kidney Cancer
Abstract
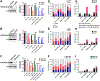
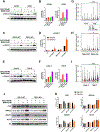
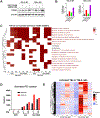
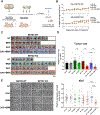
SETD2 deficiency alters the epigenetic landscape by causing depletion of H3K36me3 and plays an important role in diverse forms of cancer, most notably in aggressive and metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCC). Development of an effective treatment scheme targeting SETD2-compromised cancer is urgently needed. Considering that SETD2 is involved in DNA methylation and DNA repair, a combination treatment approach using DNA hypomethylating agents (HMA) and PARP inhibitors (PARPi) could have strong antitumor activity in SETD2-deficient kidney cancer. We tested the effects of the DNA HMA 5-aza-2'-dexoxydytidine (DAC), the PARPi talazoparib (BMN-673), and both in combination in human ccRCC models with or without SETD2 deficiency. The combination treatment of DAC and BMN-673 synergistically increased cytotoxicity in vitro in SETD2-deficient ccRCC cell lines but not in SETD2-proficient cell lines. DAC and BMN-673 led to apoptotic induction, increased DNA damage, insufficient DNA damage repair, and increased genomic instability. Furthermore, the combination treatment elevated immune responses, upregulated STING, and enhanced viral mimicry by activating transposable elements. Finally, the combination effectively suppressed the growth of SETD2-deficient ccRCC in in vivo mouse models. Together, these findings indicate that combining HMA and PARPi is a promising potential therapeutic strategy for treating SETD2-compromised ccRCC.
Significance: SETD2 deficiency creates a vulnerable epigenetic status that is targetable using a DNA hypomethylating agent and PARP inhibitor combination to suppress renal cell carcinoma, identifying a precision medicine-based approach for SETD2-compromised cancers.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest:
G. L. is a consultant for PANGEA LABORATORY. I.S.G. is a consultant for STEBA. D. I. Quinn reports employment by Abbvie Research and Development and Honoraria for advisory board participation from Merck Sharp and Dohme, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Astellas, Seagen and BMS. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures


Comment in
-
Combination of PARP and DNA methylation inhibitors as a potential personalized therapy for SETD2-mutated clear-cell renal cancers.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Jul 31;13(7):1315-1318. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-20. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39100825 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bhatt JR, Finelli A. Landmarks in the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol 2014;11:517–25 - PubMed
-
- Santos VE, da Costa WH, Bezerra SM, da Cunha IW, Nobre JQC, Brazao ES Jr., et al. Prognostic Impact of Loss of SETD2 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2021;19:339–45 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

