Usefulness of tumor perfusion on cone-beam CT after hepatic arterial infusion port implantation for evaluating tumor response to hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment
- PMID: 37695260
- PMCID: PMC10679554
- DOI: 10.4274/dir.2023.232311
Usefulness of tumor perfusion on cone-beam CT after hepatic arterial infusion port implantation for evaluating tumor response to hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment
Abstract
Purpose: To compare tumor perfusion on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) after hepatic artery infusion port implantation with the tumor response to hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
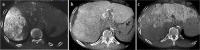
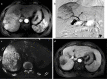
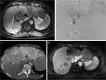
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted in patients with advanced HCC treated with HAIC from 2015 to 2020. We performed CBCT with contrast injection via a port on the day following implantation. We classified tumor perfusion on CBCT into three groups: hyperperfusion, isoperfusion, and hypoperfusion. We also evaluated tumor response to HAIC on follow-up images using RECIST 1.1 and compared it with tumor perfusion on CBCT.
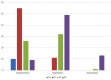
Results: This study included 206 tumors in 193 patients (mean: 60.5 years) with HCC. There were 100 hyperperfusion tumors (48.5%), 92 isoperfusion tumors (44.7%), and 14 hypoperfusion tumors (6.8%). The tumor response to HAIC included 10 tumors with a complete response (CR) (4.9%), 66 tumors with a partial response (32%), 60 tumors with stable disease (29.1%), and 70 tumors with progressive disease (34%). Hyperperfusion tumors had a 65% objective response rate (ORR) and a 92% disease control rate (DCR). Isoperfusion tumors had a 12% ORR and a 46.8% DCR, while hypoperfusion tumors had a 0% ORR and a 7.1% DCR. A CR was shown only in hyperperfusion tumors. The ORR and DCR of the three groups were different, with statistical significance (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Hyperperfusion tumors on CBCT showed a better tumor response to HAIC, with a 65% ORR in patients with HCC. Tumor perfusion on CBCT after implantation of the hepatic arterial infusion port was associated with the tumor response to HAIC.
Keywords: Cone-beam CT; hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; hepatocellular carcinoma; tumor perfusion; tumor response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10126):1163–1173. - PubMed
-
- Lyu N, Kong Y, Mu L, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin plus fluorouracil/leucovorin vs. sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69(1):60–69. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M, Ueshima K, Yokosuka O, et al. Sorafenib plus low-dose cisplatin and fluorouracil hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib alone in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (SILIUS): a randomised, open label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(6):424–432. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

