Effects of Gryllus bimaculatus and Oxya chinensis sinuosa extracts on brain damage via blood-brain barrier control and apoptosis in mice with pentylenetetrazol-induced epilepsy
- PMID: 37695764
- PMCID: PMC10495007
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291191
Effects of Gryllus bimaculatus and Oxya chinensis sinuosa extracts on brain damage via blood-brain barrier control and apoptosis in mice with pentylenetetrazol-induced epilepsy
Abstract
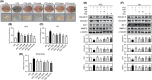
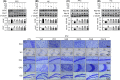
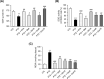
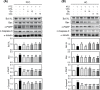
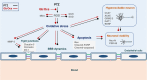
The demand for environmentally friendly foods with high nutritional value and low carbon emissions is increasing with the aging of the global population and the crisis of food resources. Edible insects are becoming increasingly well-known as such foods. This study evaluated the effects and mechanisms of Gryllus bimaculatus (Cricket) (Gb) and Oxya chinensis sinuosa (Grasshopper) (Ocs) extracts on epilepsy. A pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-induced seizure mouse model was used for the study, and Gb and Ocs extracts were administered for 29 days on alternate days at concentrations of 8 g/kg and 16 g/kg. The integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and brain edema was measured using the perfusion of Evans blue dye and brain water content. Gb and Ocs extracts prevented BBB permeabilization and cerebral edema through increasing the expression of tight junction-associated proteins in the endothelial cells and reducing water content in PTZ-treated mice. Additionally, Gb and Ocs extracts protected neurons from oxidative stress and apoptosis in different brain areas. These protective effects were demonstrated through the restoration of the expression of neuronal nuclear protein and postsynaptic density protein-95, thus increasing the levels of glutathione and superoxide dismutase, decreasing lipid peroxidation, and recovering apoptosis-associated proteins, such as Bax, cleaved PARP, and cleaved caspase-3, in epileptic mice. In addition, Gb and Ocs extracts rescued PTZ-induced hyperexcitable neurons to control mice level, as supported by the restored expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter 1, the metabotropic glutamate receptors-GRM2/3, and BDNF. This study suggested that Gb and Ocs extracts are novel medicinal candidates that can help ameliorate epilepsy by improving BBB health and preventing oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis.
Copyright: © 2023 Tran, Lee. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

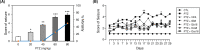

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

