Light cues induce protective anticipation of environmental water loss in terrestrial bacteria
- PMID: 37695906
- PMCID: PMC10515139
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2309632120
Light cues induce protective anticipation of environmental water loss in terrestrial bacteria
Abstract
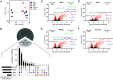
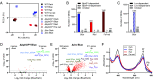
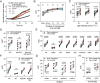
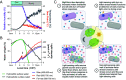
The ecological significance of light perception in nonphotosynthetic bacteria remains largely elusive. In terrestrial environments, diurnal oscillations in light are often temporally coupled to other environmental changes, including increased temperature and evaporation. Here, we report that light functions as an anticipatory cue that triggers protective adaptations to tolerate a future rapid loss of environmental water. We demonstrate this photo-anticipatory stress tolerance in leaf-associated Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae (Pss) and other plant- and soil-associated pseudomonads. We found that light influences the expression of 30% of the Pss genome, indicating that light is a global regulatory signal, and this signaling occurs almost entirely via a bacteriophytochrome photoreceptor that senses red, far-red, and blue wavelengths. Bacteriophytochrome-mediated light control disproportionally up-regulates water-stress adaptation functions and confers enhanced fitness when cells encounter light prior to water limitation. Given the rapid speed at which water can evaporate from leaf surfaces, such anticipatory activation of a protective response enhances fitness beyond that of a reactive stress response alone, with recurring diurnal wet-dry cycles likely further amplifying the fitness advantage over time. These findings demonstrate that nonphotosynthetic bacteria can use light as a cue to mount an adaptive anticipatory response against a physiologically unrelated but ecologically coupled stress.
Keywords: adaptive prediction; anticipatory regulation; light sensing; photoreceptor; stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Davis S. J., Vener A. V., Vierstra R. D., Bacteriophytochromes: Phytochrome-like photoreceptors from nonphotosynthetic eubacteria. Science 286, 2517–2520 (1999). - PubMed
-
- van der Horst M. A., Key J., Hellingwerf K. J., Photosensing in chemotrophic, non-phototrophic bacteria: Let there be light sensing too. Trends Microbiol. 15, 554–562 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Mandalari C., Losi A., Gartner W., Distance-tree analysis, distribution and co-presence of bilin- and flavin-binding prokaryotic photoreceptors for visible light. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 12, 1144–1157 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Bhoo S. H., Davis S. J., Walker J., Karniol B., Vierstra R. D., Bacteriophytochromes are photochromic histidine kinases using a biliverdin chromophore. Nature 414, 776–779 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Swartz T. E., et al. , Blue-light-activated histidine kinases: Two-component sensors in bacteria. Science 317, 1090–1093 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

