Lumicrine signaling: Extracellular regulation of sperm maturation in the male reproductive tract lumen
- PMID: 37696504
- PMCID: PMC11447831
- DOI: 10.1111/gtc.13066
Lumicrine signaling: Extracellular regulation of sperm maturation in the male reproductive tract lumen
Abstract
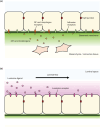
The behaviors of cells, tissues, and organs are controlled by the extracellular environment in addition to their autonomous regulatory system. Dysfunction of extracellular regulatory mechanisms affects not only the development and survival of organisms but also successful reproduction. In this review article, a novel extracellular regulatory mechanism regulating the mammalian male reproductive ability will be briefly summarized. In terrestrial vertebrates, spermatozoa generated in the testis are transported through the lumen of the male reproductive tract and become functionally mature during the transport. Recent studies with gene-modified animals are unveiling the luminal extracellular environment of the reproductive tract to function not only as the pathway of sperm transport and the site of sperm maturation but also as the channel for cellular communication to regulate sperm maturation. Of special interest is the molecular mechanism of lumicrine signaling, a transluminal secreted signal transduction in the male reproductive tract lumen as a master regulator of sperm maturation and male reproductive ability. The general significance of such transluminal signaling in the context of cell biology will also be discussed.
Keywords: Lumicrine; NELL2; epididymis; signal transduction; sperm maturation.
© 2023 The Author. Genes to Cells published by Molecular Biology Society of Japan and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Da Ros, V. G. , Maldera, J. A. , Willis, W. D. , Cohen, D. J. , Goulding, E. H. , Gelman, D. M. , Rubinstein, M. , Eddy, E. M. , & Cuasnicu, P. S. (2008). Impaired sperm fertilizing ability in mice lacking Cysteine‐RIch Secretory Protein 1 (CRISP1). Developmental Biology, 320, 12–18. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.03.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

