Targeting the Liver with Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for the Treatment of Systemic Diseases of Liver Origin
- PMID: 37696583
- PMCID: PMC10753797
- DOI: 10.1124/pharmrev.123.000815
Targeting the Liver with Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for the Treatment of Systemic Diseases of Liver Origin
Abstract
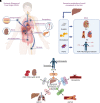
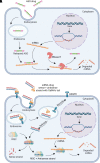
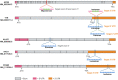
Systemic diseases of liver origin (SDLO) are complex diseases in multiple organ systems, such as cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, endocrine, renal, respiratory, and sensory organ systems, caused by irregular liver metabolism and production of functional factors. Examples of such diseases discussed in this article include primary hyperoxaluria, familial hypercholesterolemia, acute hepatic porphyria, hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis, hemophilia, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, α-1 antitrypsin deficiency-associated liver disease, and complement-mediated diseases. Nucleic acid therapeutics use nucleic acids and related compounds as therapeutic agents to alter gene expression for therapeutic purposes. The two most promising, fastest-growing classes of nucleic acid therapeutics are antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). For each listed SDLO disease, this article discusses epidemiology, symptoms, genetic causes, current treatment options, and advantages and disadvantages of nucleic acid therapeutics by either ASO or siRNA drugs approved or under development. Furthermore, challenges and future perspectives on adverse drug reactions and toxicity of ASO and siRNA drugs for the treatment of SDLO diseases are also discussed. In summary, this review article will highlight the clinical advantages of nucleic acid therapeutics in targeting the liver for the treatment of SDLO diseases. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Systemic diseases of liver origin (SDLO) contain rare and common complex diseases caused by irregular functions of the liver. Nucleic acid therapeutics have shown promising clinical advantages to treat SDLO. This article aims to provide the most updated information on targeting the liver with antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNA drugs. The generated knowledge may stimulate further investigations in this growing field of new therapeutic entities for the treatment of SDLO, which currently have no or limited options for treatment.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Adams DGonzalez-Duarte AO’Riordan WDYang C-CUeda MKristen AVTournev ISchmidt HHCoelho TBerk JL, et al. (2018) Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 379:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Adams DTournev ILTaylor MSCoelho TPlanté-Bordeneuve VBerk JLGonzález-Duarte AGillmore JDLow S-CSekijima Y, et al. ; HELIOS-A Collaborators (2023) Efficacy and safety of vutrisiran for patients with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. Amyloid 30:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
