Yoga maintains Th17/Treg cell homeostasis and reduces the rate of T cell aging in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 37696876
- PMCID: PMC10495372
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42231-w
Yoga maintains Th17/Treg cell homeostasis and reduces the rate of T cell aging in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
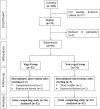
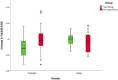
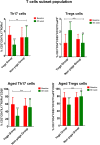
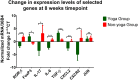
The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by a Th17/Treg cell imbalance. A pro-inflammatory cytokine milieu that promotes the continued proliferation of Th17 cells is related to the development of autoinflammation. In RA, T cells have several hallmarks of cellular aging, and they accumulate DNA damage, predisposing to the occurrence of mutations and epigenetic alterations. Since the onset, progression, and treatment response are influenced by a variety of external stressors and environmental factors, this study aimed to evaluate the impact of 8-week yoga practice on disease severity, T cell subsets, markers of T cell ageing and inflammation, epigenetic alterations and gene expression patterns in active RA patients on standard disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). A total of 64 participants with active RA were randomized into 2 groups, yoga group (n = 32) or non-yoga group (n = 32); that were assessed for disease severity, at baseline and after 8 week duration, for Disease Activity Score (DAS28-ESR), T cell subsets [Th17 (CD3+ CD4+ IL17+ RORγt+) cells and Treg (CD3+ CD4+ CD25+ CD127-Foxp3+) cells], markers of T cell aging [aged Th17 cells (CD3+ CD4+ IL17+ RORγt+ CD28-) and aged Treg cells (CD3+ CD4+ CD25+ CD127-Foxp3+ CD28-)], pro-inflammatory markers [IL-6, and IL-17], anti-inflammatory markers [TGF-β, and IL-10], epigenetic alterations [5-methyl cytosine, 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine, and HDAC1] and gene expression patterns [RORγt, FoxP3, IL-17, IL-6, TGF-β, CXCL2, CXCR2, and JUN]. In yoga group, there was a significant improvement in DAS28-ESR scores at the end of 8-weeks of yoga program. The Th17 cells and aged T cell subsets showed a significant decline whereas Treg cell population showed a significant elevation in yoga group. There were significant improvements observed in epigenetic markers as well as inflammatory markers post 8-weeks of yoga practice. The yoga group showed downregulation of RORγt, IL-17, IL-6, CXCL2, CXCR2, and upregulation of FoxP3 and TGF-β transcripts. Yoga enables the maintenance of immune-homeostasis as evident by increased Treg cell population and reduced Th17 cell population. Yoga reduces the rate of immunological aging in T cells, as seen by the reduction in population of aged Th17 cells and aged Treg cells. Yoga positively modifies transcriptome and epigenome by normalization of various inflammatory markers, gene expression patterns and epigenetic alterations. Taken together, yoga reduces RA severity, and aids in immune-modulation and hence can be beneficial as an adjunct therapy.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription Factor Analysis to Investigate Immunosenescence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2857:79-87. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4128-6_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39348056
-
NF-κB-driven miR-34a impairs Treg/Th17 balance via targeting Foxp3.J Autoimmun. 2019 Aug;102:96-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.04.018. Epub 2019 May 23. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 31130368
-
Upregulated Expression of microRNA-16 Correlates with Th17/Treg Cell Imbalance in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.DNA Cell Biol. 2016 Dec;35(12):853-860. doi: 10.1089/dna.2016.3349. Epub 2016 Nov 22. DNA Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27875659
-
FOXP3 and RORγt: transcriptional regulation of Treg and Th17.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 May;11(5):536-42. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.11.008. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21081189 Review.
-
The Functional Stability of FOXP3 and RORγt in Treg and Th17 and Their Therapeutic Applications.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;107:155-189. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28215223 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunosenescence and cancer: molecular hallmarks, tumor microenvironment remodeling, and age-specific immunotherapy challenges.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 Aug 22;18(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01735-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40846970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Yoga on Gene Expression: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2025 Apr 21;17(4):e82690. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82690. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40400827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Augmenting regulatory T cells: new therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 23;15:1312919. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1312919. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38322264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Factor Analysis to Investigate Immunosenescence in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2857:79-87. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4128-6_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39348056
-
Assessing the causal role of immune traits in rheumatoid arthritis by bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 16;16(10):8687-8696. doi: 10.18632/aging.205833. Epub 2024 May 16. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38761178 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

