Unconventional immune cells in the gut mucosal barrier: regulation by symbiotic microbiota
- PMID: 37696893
- PMCID: PMC10545787
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-01088-9
Unconventional immune cells in the gut mucosal barrier: regulation by symbiotic microbiota
Abstract
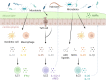
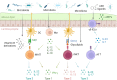
The mammalian gut is the most densely colonized organ by microbial species, which are in constant contact with the host throughout life. Hosts have developed multifaceted cellular and molecular mechanisms to distinguish and respond to benign and pathogenic bacteria. In addition to relatively well-characterized innate and adaptive immune cells, a growing body of evidence shows additional important players in gut mucosal immunity. Among them, unconventional immune cells, including innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) and unconventional T cells, are essential for maintaining homeostasis. These cells rapidly respond to bacterial signals and bridge the innate immunity and adaptive immunity in the mucosal barrier. Here, we focus on the types and roles of these immune cells in physiological and pathological conditions as prominent mechanisms by which the host immune system communicates with the gut microbiota in health and diseases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gut microbiota as a key regulator of intestinal mucosal immunity.Life Sci. 2024 May 15;345:122612. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122612. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38588949 Review.
-
The interaction of intestinal microbiota and innate lymphoid cells in health and disease throughout life.Immunology. 2020 Jan;159(1):39-51. doi: 10.1111/imm.13138. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 31777064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host-microbiota interactions in the intestine.Dig Dis. 2015;33(2):131-136. doi: 10.1159/000369534. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Dig Dis. 2015. PMID: 25925913 Review.
-
Crosstalk between the gut microbiota and innate lymphoid cells in intestinal mucosal immunity.Front Immunol. 2023 May 25;14:1171680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171680. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37304260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota Modulation on Intestinal Mucosal Adaptive Immunity.J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 3;2019:4735040. doi: 10.1155/2019/4735040. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31687412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Food antigens suppress small intestinal tumorigenesis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1373766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373766. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39359724 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-lung axis in asthma and obesity: role of the gut microbiome.Front Allergy. 2025 Jun 16;6:1618466. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1618466. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40589493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of gut barrier dysfunction in postoperative complications in liver transplantation: pathophysiological and therapeutic considerations.Infection. 2024 Jun;52(3):723-736. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02182-4. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38324146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Driven Modulation of Mucosal Immunity and Interplay with the Microbiome.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 12;35:e2404033. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2504.04033. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40537897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galactooligosaccharide Mediates NF-κB Pathway to Improve Intestinal Barrier Function and Intestinal Microbiota.Molecules. 2023 Nov 15;28(22):7611. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227611. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38005333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fan, Y. & Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.19, 55–71 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology - 10th Edition. https://www.elsevier.com/books/cellular-and-molecular-immunology/abbas/9... (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

