Dynamic lipidome alterations associated with human health, disease and ageing
- PMID: 37697054
- PMCID: PMC10513930
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00880-1
Dynamic lipidome alterations associated with human health, disease and ageing
Abstract
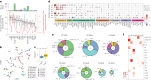
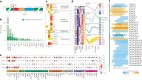
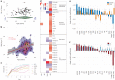
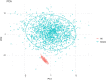
Lipids can be of endogenous or exogenous origin and affect diverse biological functions, including cell membrane maintenance, energy management and cellular signalling. Here, we report >800 lipid species, many of which are associated with health-to-disease transitions in diabetes, ageing and inflammation, as well as cytokine-lipidome networks. We performed comprehensive longitudinal lipidomic profiling and analysed >1,500 plasma samples from 112 participants followed for up to 9 years (average 3.2 years) to define the distinct physiological roles of complex lipid subclasses, including large and small triacylglycerols, ester- and ether-linked phosphatidylethanolamines, lysophosphatidylcholines, lysophosphatidylethanolamines, cholesterol esters and ceramides. Our findings reveal dynamic changes in the plasma lipidome during respiratory viral infection, insulin resistance and ageing, suggesting that lipids may have roles in immune homoeostasis and inflammation regulation. Individuals with insulin resistance exhibit disturbed immune homoeostasis, altered associations between lipids and clinical markers, and accelerated changes in specific lipid subclasses during ageing. Our dataset based on longitudinal deep lipidome profiling offers insights into personalized ageing, metabolic health and inflammation, potentially guiding future monitoring and intervention strategies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.P.S. is a co-founder and on the advisory board of Personalis, SensOmics, January AI, Filtricine, Qbio, Protos, iollo, RTHM and Mirive. M.P.S. is on the advisory board of Jupiter, Abbratech, Neuvivo and Mitrix. D.H. has financial interests in Seer and PrognomiQ. K.C. is currently an AstraZeneca employee. A.A.M. is currently an employee of Google. K.J.W. is a consultant for Verso Biosciences, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plasma lipidomics in subjects with combat posttraumatic stress disorder.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Aug 20;189:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.07.012. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35918015
-
Dyslipidemia, but not hyperglycemia and insulin resistance, is associated with marked alterations in the HDL lipidome in type 2 diabetic subjects in the DIWA cohort: impact on small HDL particles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1831(11):1609-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23896361
-
The maternal blood lipidome is indicative of the pathogenesis of severe preeclampsia.J Lipid Res. 2021;62:100118. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100118. Epub 2021 Sep 20. J Lipid Res. 2021. PMID: 34547287 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomics in diabetes.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022 Apr 1;29(2):124-130. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000704. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022. PMID: 34954721 Review.
-
Adipose tissue insulin resistance and lipidome alterations as the characterizing factors of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2022 Mar;52(3):e13695. doi: 10.1111/eci.13695. Epub 2021 Dec 7. Eur J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 34695228 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal and mediating effects of lipid and facial aging: association study integrating GWAS, eQTL, mQTL, and pQTL data.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Oct 21;23(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02328-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39434152 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted lipidomics reveals novel HDL metabotypes and lipid-clinical correlates.J Lipid Res. 2024 Dec;65(12):100678. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100678. Epub 2024 Oct 25. J Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 39490932 Free PMC article.
-
The link between alterations in circadian rhythms and lipid metabolism in bipolar disorder: the hypothesis of lipid droplets.Braz J Psychiatry. 2024;46:e20243670. doi: 10.47626/1516-4446-2024-3670. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Braz J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39102528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative cross-tissue analysis unveils complement-immunoglobulin augmentation and dysbiosis-related fatty acid metabolic remodeling during mammalian aging.Imeta. 2025 Apr 12;4(3):e70027. doi: 10.1002/imt2.70027. eCollection 2025 Jun. Imeta. 2025. PMID: 40469517 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted lipidomics profiling provides novel insights into pediatric patients with sepsis: an exploratory study.Metabolomics. 2025 Apr 26;21(3):59. doi: 10.1007/s11306-025-02255-x. Metabolomics. 2025. PMID: 40281388 Free PMC article.

