Psychosocial-spiritual well-being is related to resilience and mindfulness in patients with severe and/or life-limiting medical illness
- PMID: 37697251
- PMCID: PMC10494355
- DOI: 10.1186/s12904-023-01258-6
Psychosocial-spiritual well-being is related to resilience and mindfulness in patients with severe and/or life-limiting medical illness
Abstract
Background: Improvement of psychosocial-spiritual well-being in patients with life-threatening or life-limiting illness is desirable. Resilience and mindfulness are considered to be helpful for enhancing psychosocial-spiritual well-being. Mindfulness-based interventions have been shown to promote resilience to stress and enhance well-being. However, in medical patients, evidence for the associations between mindfulness and resilience is lacking. We hypothesize patients with higher levels of psychosocial-spiritual well-being demonstrate greater resilience and mindfulness.
Methods: 200 patients (mean age = 50.2, SD = 15.5) with serious and or life-limiting illnesses were recruited from the NIH Clinical Center. Patients completed a demographic questionnaire, the NIH-HEALS measure of psychosocial-spiritual well-being, the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC-10), and the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale (MAAS). The demographic questionnaire also included a question on current stress level.
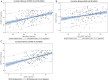
Results: The NIH-HEALS was positively correlated to CD-RISC-10 (rs=0.44, p < 0.001) and MAAS (rs=0.32, p < 0.001). These findings were consistent across all three NIH-HEALS factors. Additionally, CD-RISC-10 and MAAS demonstrated a meaningful relationship to each other (rs=0.46, p < 0.001). All three constructs were inversely related to current stress level.
Conclusions: Findings suggest that there is a meaningful relationship between psychosocial-spiritual well-being, mindfulness, and resilience. Mindfulness and resilience are positively correlated in a medical population. Clinical interventions aimed at enhancing psychosocial-spiritual well-being through mindfulness and resilience can be highly promising for patients with severe and or life limiting illness.
Keywords: Mindfulness; Psychosocial-spiritual well-being; Resilience.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resilience and spiritual well-being as resources for coping with radiotherapy and surviving in patients with glioblastoma.Palliat Support Care. 2024 Nov 5;23:e10. doi: 10.1017/S1478951524001111. Palliat Support Care. 2024. PMID: 39497355
-
Revitalizing Minds: Exploring the Transformative Power of Mindfulness-Based Nursing Interventions on Depression and Resilience in Oncology Patients-A Quasiexperimental Approach.Int J Nurs Pract. 2025 Apr;31(2):e70005. doi: 10.1111/ijn.70005. Int J Nurs Pract. 2025. PMID: 40068938
-
How mindfulness affects benign and malicious envy from the perspective of the mindfulness reperceiving model.Scand J Psychol. 2020 Jun;61(3):436-442. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12596. Epub 2019 Dec 15. Scand J Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31840272
-
Gender Differences in Psycho-Social-Spiritual Healing.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019 Nov;28(11):1513-1521. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2019.7837. Epub 2019 Sep 6. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019. PMID: 31502927 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of mindfulness and self-compassion on anxiety and depression: The mediating role of resilience.Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2021 May-Aug;21(2):100229. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2021.100229. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33767736 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring Spiritual Needs and Loneliness Among Acutely Hospitalized Patients with Chronic Illnesses: An Observational Study Across Three Waves of the COVID-19 Epidemic in Taiwan.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 21;61(4):770. doi: 10.3390/medicina61040770. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40283061 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic Review of Spirituality Tools Based on Psychometric Qualities and Recommendations for Future Research.J Relig Health. 2025 Apr;64(2):1257-1275. doi: 10.1007/s10943-024-02220-3. Epub 2024 Dec 26. J Relig Health. 2025. PMID: 39724494
-
Effects of a combined nature-based and audio-based virtual mindfulness intervention on stress and wellbeing of COVID-19 healthcare workers: a randomized controlled trial.PeerJ. 2025 May 23;13:e19109. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19109. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40421373 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Spiritual Care Education on Leukemia Patients' Post-traumatic Growth and Resilience in Iran: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Relig Health. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s10943-025-02393-5. Online ahead of print. J Relig Health. 2025. PMID: 40684002
-
The influence of spirituality on psychological resilience in cancer patients undergoing oncological treatment: a cross-sectional study.BMC Palliat Care. 2025 May 14;24(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12904-025-01768-5. BMC Palliat Care. 2025. PMID: 40369480 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

