Potential of miR-181a-5p and miR-630 as clinical biomarkers in NSCLC
- PMID: 37697308
- PMCID: PMC10496384
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-11365-5
Potential of miR-181a-5p and miR-630 as clinical biomarkers in NSCLC
Abstract
Background: The development of drug resistance and high mortality rates are the major problems observed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Biomarkers indicating and predicting disease development towards these unfavorable directions are therefore on high demand. Many studies have demonstrated that changes in miRNAs expression may be associated with a response to treatment and disease prognosis, thus suggesting its potential biomarker value for a broad spectrum of clinical applications. The aim of the present study was to investigate the expression level of miR-181a-5p, miR-630, and its targets in NSCLC tumor tissue and plasma samples; and to analyze its association with NSCLC patient's response to treatment and disease prognosis.
Methods: The study was performed in 89 paired tissue specimens and plasma samples obtained from NSCLC patients who underwent surgical treatment at the Department of Thoracic Surgery and Oncology of the National Cancer Institute. Analysis of miR-181a-5p and miR-630 expression was performed by qRT-PCR using TaqMan miRNA specific primers. Whereas BCL2, LMO3, PTEN, SNAI2, WIF1 expression levels were identified with KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Kit. Each sample was examined in triplicate and calculated following the 2-ΔΔCt method. When the p-value was less than 0.05, the differences were considered statistically significant.
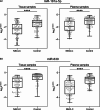
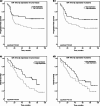
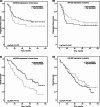
Results: It was found that miR-181a-5p and miR-630 expression levels in NSCLC tissue and plasma samples were significantly decreased compared with control samples. Moreover, patients with low miR-181a-5p expression in tumor tissue and plasma had longer PFS rates than those with high miRNA expression. Decreased miR-630 expression in tumor was statistically significantly associated with better NSCLC patients' OS. In addition, the expression of miR-181a-5p, as well as miR-630 in tumor tissue, are the statistically significant variables for NSCLC patients' OS. Moreover, in NSCLC patient plasma samples circulating miR-181a-5p can be evaluated as significant independent prognostic factors for OS and PFS.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate the miR-181a-5p and miR-630 expression levels have the potential to prognose and predict and therefore improve the treatment individualization and the outcome of NSCLC patients. Circulating miR-181a-5p has the potential clinical value as a non-invasive biomarker for NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC; Non-invasive clinical biomarkers; Response to treatment; miR-181a-5p; miR-630.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx (Accessed: 30 August 2022).
-
- Global Cancer Observatory. : Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Lyon, France. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (Accessed: 30 August 2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

