Strengthening antimicrobial resistance surveillance systems: a scoping review
- PMID: 37697310
- PMCID: PMC10496311
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08585-2
Strengthening antimicrobial resistance surveillance systems: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an emerging global public health crisis. Surveillance is a fundamental component in the monitoring and evaluation of AMR mitigation endeavours. The primary aim of the scoping review is to identify successes, barriers, and gaps in implementing AMR surveillance systems and utilising data from them.
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, SCOPUS, and EMBASE databases were searched systematically to identify literature pertaining to implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of AMR surveillance systems. A thematic analysis was conducted where themes within the literature were inductively grouped based on the described content.
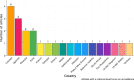
Results: The systematic search yielded 639 journal articles for screening. Following deduplication and screening, 46 articles were determined to be appropriate for inclusion. Generally, most studies focused on human AMR surveillance (n = 38, 82.6%). Regionally, there was equal focus on low- and middle-income countries (n = 7, 15.2%) and trans-national contexts (n = 7, 14.5%). All included articles (n = 46, 100.0%) discussed barriers to either implementing or utilising AMR surveillance systems. From the scoping review, 6 themes emerged: capacity for surveillance, data infrastructure, policy, representativeness, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability. Data infrastructure was most frequently discussed as problematic in evaluation of surveillance systems (n = 36, 75.0%). The most frequent success to surveillance system implementation was stakeholder engagement (n = 30, 65.2%).
Conclusions: Experiences of AMR surveillance systems are diverse across contexts. There is a distinct separation of experiences between systems with emerging surveillance systems and those with established systems. Surveillance systems require extensive refinement to become representative and meet surveillance objectives.
Keywords: AMR; AMR scoping review; Antimicrobial Resistance; Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance; Experiences; Gaps; Strengths; Surveillance.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
No conflict of interests to declare.
Figures




References
-
- WHO.: Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. World Health Organization. [https://ahpsr.who.int/publications/i/item/global-action-plan-on-antimicr...]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

