Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA and nucleocapsid concentrations in samples used in INSTAND external quality assessment schemes
- PMID: 37697348
- PMCID: PMC10496272
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-023-06497-7
Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA and nucleocapsid concentrations in samples used in INSTAND external quality assessment schemes
Abstract
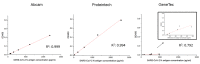
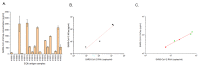
Objective: In routine clinical laboratories, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection is determined by reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR). In the COVID pandemic, a wide range of antigen detection tests were also in high demand. We investigated the correlation between SARS-CoV-2 NCap antigen and N gene concentration by analyzing samples from several INSTAND external quality assessment (EQA) schemes starting in March 2021. The absolute N gene concentration was measured using reverse transcriptase digital PCR (RT-dPCR) as reference value. Moreover, the performance of five commercial ELISA tests using an EQA inactivated SARS-CoV-2 sample at different concentrations was assessed on the basis of these reference values.
Results: Quantitative ELISA and RT-dPCR results showed a good correlation between SARS-CoV-2 NCap antigen and RNA concentration, but this correlation varies among SARS-CoV-2 isolates. A direct correlation between SARS-CoV-2 NCap antigen concentration and genome concentration should not be generally assumed.
Conclusion: Further correlation studies between SARS-CoV-2 RNA and NCap antigen concentrations are needed, particularly in clinical samples and for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, to support the monitoring and improvement of antigen testing.
Keywords: ELISA; Nucleocapsid (NCap) antigen; Quantification; RNA; RT-dPCR; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Heinz Zeichhardt declares that he is majority owner and managing director of GBD Gesellschaft fuer Biotechnologische Diagnostik mbH, Berlin, and owner and managing director of IQVD GmbH - Institut fuer Qualitaetssicherung, Berlin. All other authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays, Interim guidance., 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/antigen-detection-in-the-diagnos.... Aaccessed 26 March 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

