Predictive overfitting in immunological applications: Pitfalls and solutions
- PMID: 37697867
- PMCID: PMC10498807
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2251830
Predictive overfitting in immunological applications: Pitfalls and solutions
Abstract
Overfitting describes the phenomenon where a highly predictive model on the training data generalizes poorly to future observations. It is a common concern when applying machine learning techniques to contemporary medical applications, such as predicting vaccination response and disease status in infectious disease or cancer studies. This review examines the causes of overfitting and offers strategies to counteract it, focusing on model complexity reduction, reliable model evaluation, and harnessing data diversity. Through discussion of the underlying mathematical models and illustrative examples using both synthetic data and published real datasets, our objective is to equip analysts and bioinformaticians with the knowledge and tools necessary to detect and mitigate overfitting in their research.
Keywords: Overfitting; data diversity; dimension reduction; distributionally robust optimization; model evaluation; regularization.
Conflict of interest statement
SHK receives consulting fees from Peraton. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

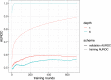
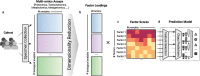
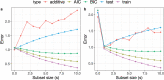
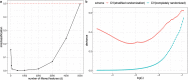

References
-
- Fourati S, Tomalin LE, Mulè MP, Chawla DG, Gerritsen B, Rychkov D, Henrich E, Miller HE, Hagan T, Diray-Arce J, et al. Pan-vaccine analysis reveals innate immune endotypes predictive of antibody responses to vaccination. Nat Immunol. 2022;23(12):1777–87. doi:10.1038/s41590-022-01329-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
