Recent Advances in Anti-Atherosclerosis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Nanomaterial-Derived Drug Formulations
- PMID: 37698552
- PMCID: PMC10582432
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202302918
Recent Advances in Anti-Atherosclerosis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Nanomaterial-Derived Drug Formulations
Abstract
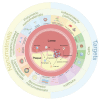
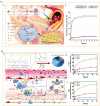
Atherosclerosis, the leading cause of death worldwide, is responsible for ≈17.6 million deaths globally each year. Most therapeutic drugs for atherosclerosis have low delivery efficiencies and significant side effects, and this has hampered the development of effective treatment strategies. Diversified nanomaterials can improve drug properties and are considered to be key for the development of improved treatment strategies for atherosclerosis. The pathological mechanisms underlying atherosclerosis is summarized, rationally designed nanoparticle-mediated therapeutic strategies, and potential future therapeutic targets for nanodelivery. The content of this study reveals the potential and challenges of nanoparticle use for the treatment of atherosclerosis and highlights new effective design ideas.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; drug; nanodelivery; nanoparticles; therapeutic strategy.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Libby P., Ridker P. M., Hansson G. K., Nature 2011, 473, 317. - PubMed
-
- Libby P., Nature 2002, 420, 868. - PubMed
-
- Virani S. S., Alonso A., Benjamin E. J., Bittencourt M. S., Callaway C. W., Carson A. P., Chamberlain A. M., Chang A. R., Cheng S., Delling F. N., Djousse L., Elkind M. S. V., Ferguson J. F., Fornage M., Khan S. S., Kissela B. M., Knutson K. L., Kwan T. W., Lackland D. T., Lewis T. T., Lichtman J. H., Longenecker C. T., Loop M. S., Lutsey P. L., Martin S. S., Matsushita K., Moran A. E., Mussolino M. E., Perak A. M., Rosamond W. D., et al., Circulation 2020, 141, e139. - PubMed
-
- Null N., Reiner Z., Catapano A. L., De Backer G., Graham I., Taskinen M.‐R., Wiklund O., Agewall S., Alegria E., Chapman M. J., Durrington P., Erdine S., Halcox J., Hobbs R., Kjekshus J., Filardi P. P., Riccardi G., Storey R. F., Wood D., Bax J., Vahanian A., Auricchio A., Baumgartner H., Ceconi C., Dean V., Deaton C., Fagard R., Filippatos G., Funck‐Brentano C., Hasdai D., et al., Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1769. - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard B. G., Nicholls S. J., Langsted A., Ray K. K., Tybjærg‐Hansen A., Nat Rev Cardiol 2018, 15, 261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 20ZR1420000/Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai
- 21S21902100/Science and Technology Support Project in Biomedical Field of Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- 2021-HSD-8-6-001/Baoshan Zhaohui New Drug R & D and Transformation Functional Platform
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
