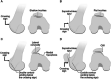
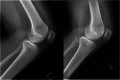
Sulcus-Deepening Trochleoplasty for High-Grade Trochlear Dysplasia: Demystifying the Procedure-a Review of the Current Literature
- PMID: 37698757
- PMCID: PMC10587046
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-023-09868-6
Sulcus-Deepening Trochleoplasty for High-Grade Trochlear Dysplasia: Demystifying the Procedure-a Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
Purpose of review: The most common and biomechanically influential pathoanatomic risk factor for recurrent patellofemoral instability is trochlear dysplasia. Sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty is a procedure developed to address high-grade trochlear dysplasia in the setting of patellofemoral instability. The purpose of this paper is to outline the current classification and surgical management of trochlear dysplasia as well as to review the current literature on the clinical outcomes and complications of sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty.
Recent findings: This review outlines the most recent literature reporting evidence behind the decision-making to perform a trochleoplasty in the setting of patellofemoral instability and high-grade trochlear dysplasia. Critical parameters include grade of trochlear dysplasia, severity of symptoms, pertinent physical examination findings, surgical techniques, modifications for skeletally immature patients, and considerations for the revision setting. Historic studies have elicited concerns regarding high reported complication rates for trochleoplasty; however, recent studies consistently report good clinical outcomes and acceptable complication rates, similar to those of other patellar stabilizing procedures. The addition of a trochleoplasty in patients with high-grade dysplasia results in a lower re-dislocation rate, significant improvements in patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) as well as high levels of patient satisfaction and return to sport. The use of sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty for the treatment of high-grade dysplasia and recurrent patellofemoral instability is a well-established technique with good outcomes and an acceptable complication profile. In patients with high-grade dysplasia, trochleoplasty results in lower re-dislocation rates, high patient satisfaction scores, and good clinical and functional outcomes. An understanding of trochleoplasty and its indications should be in the armamentarium of surgeons treating patellofemoral instability.
Keywords: MPFL; Medial patellofemoral ligament; Patellar instability; Patellofemoral instability; Trochlear dysplasia; Trochleoplasty.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Magdalena Tarchala, Sarah Kerslake, and Laurie Hiemstra declare that they have no conflict of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thin Flap Trochleoplasty With Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellofemoral Instability With High-Grade Trochlear Dysplasia: A Series of 63 Consecutive Cases.Am J Sports Med. 2025 Mar;53(4):832-838. doi: 10.1177/03635465251314882. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Am J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 39910743
-
Midterm results of comprehensive surgical reconstruction including sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in recurrent patellar dislocations with high-grade trochlear dysplasia.Am J Sports Med. 2013 May;41(5):998-1004. doi: 10.1177/0363546513482302. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Am J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23589587
-
Influence of Sulcus-Deepening Trochleoplasty on Patellofemoral Cartilage Integrity in Patients With Severe Trochlear Dysplasia at Short-term to Midterm Follow-up: A Case-Control Study.Orthop J Sports Med. 2025 Apr 2;13(4):23259671251326052. doi: 10.1177/23259671251326052. eCollection 2025 Apr. Orthop J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40182561 Free PMC article.
-
Trochleoplasty: Indications in patellar dislocation with high-grade dysplasia. Surgical technique.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022 Feb;108(1S):103160. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2021.103160. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 34863959 Review.
-
Sulcus-Deepening Trochleoplasty as an Isolated or Combined Treatment Strategy for Patellar Instability and Trochlear Dysplasia: A Systematic Review.Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2020 Aug 19;2(5):e661-e669. doi: 10.1016/j.asmr.2020.06.009. eCollection 2020 Oct. Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 33135008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparable postoperative outcomes in patients treated with either open or arthroscopic trochleoplasty for patella dysplasia.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024 Dec 2;36(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s43019-024-00247-0. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39623489 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Patellar Dysplasia and Postoperative Pain After Mini-Open, Thin-Flap Trochleoplasty: A Retrospective Analysis of 75 Consecutive Cases.Orthop J Sports Med. 2024 Aug 27;12(8):23259671241270352. doi: 10.1177/23259671241270352. eCollection 2024 Aug. Orthop J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39315033 Free PMC article.
-
Patellofemoral Instability in the Pediatric and Adolescent Population: From Causes to Treatments.Children (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;11(10):1261. doi: 10.3390/children11101261. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting two-year return-to-sport failure after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction in patellar dislocation patients with bone abnormalities.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 18;19(1):766. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05253-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39558386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- •• Hiemstra LA, Kerslake S, Lafave MR. Quality-of-life outcomes of patients following patellofemoral stabilization surgery: the influence of trochlear dysplasia. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(9):887–93. This paper is the first to follow patients with trochlear dysplasia after MPFL reconstruction, using a disease-specific quality of life measure, to determine the threshold at which patients have poorer outcomes with trochlear dysplasia. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials