Evaluating the effects of geochemical and anthropogenic factors on the concentration and treatability of heavy metals in Awash River and Lake Beseka, Ethiopia: arsenic and molybdenum issues
- PMID: 37698767
- PMCID: PMC10497432
- DOI: 10.1007/s10661-023-11674-z
Evaluating the effects of geochemical and anthropogenic factors on the concentration and treatability of heavy metals in Awash River and Lake Beseka, Ethiopia: arsenic and molybdenum issues
Abstract
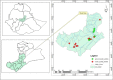
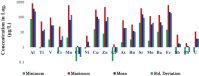
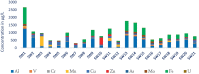
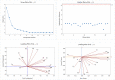
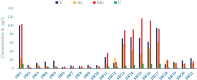
In the Awash River basin (Ethiopia), massive urbanization and industrialization, driven by rapid development and human settlement, are detrimental to the environment and human health as pollutants such as heavy metals (HMs) find their way into water bodies without proper treatment. The purpose of this study was to assess the HMs content and pollution sources within the basin. In this context, a total of 205 samples were collected from 21 surface water sampling stations. Heavy metal concentrations were measured using the Perkin Elmer NexION 350 ICP-MS with inductively coupled plasma. Findings demonstrate that high levels of HMs, such as Al, Mn, Mo, As, V, Fe, and Ba were exhibited with the value of 1257 μg/L, 626.8 μg/L, 116.7 μg/L, 61.2 μg/L, 100.5 μg/L, 1082.7 μg/L, and 211.7 μg/L, respectively. Among 20 HMs analyzed, 20% of the parameters within the study area were above the WHO limit for drinking water; Al (157 μg/L), V (100.5 μg/L), Fe (1082.7 μg/L), Mn (626.8 μg/L), and Mo (103.8 μg/L) were exhibited at sites along the river system. Likewise, 57% of water samples showed high values of As at many stations down the river systems. In particular, high HM concentrations seen in the upper Awash are primarily controlled by anthropogenic activities such as untreated industrial, agricultural, and domestic discharges, while the high HM concentrations in the middle Awash samples were likely due to the influence from the Lake Beseka that has high HM concentrations due to geological process. In conclusion, securing potable water for the rapidly increasing population in Addis Ababa and in the watersheds of Awash is unsafe to sustain the environment and the human health.
Keywords: Arsenic; Awash River; Heavy metals; Lake Beseka; Molybdenum.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Alcaine AA, Schulz C, Bundschuh J, Jacks G, Thunvik R, Gustafsson J-P, Mörth C-M, Sracek O, Ahmad A, Bhattacharya P. Hydrogeochemical controls on the mobility of arsenic, fluoride and other geogenic co-contaminants in the shallow aquifers of northeastern La Pampa Province in Argentina. Science of the Total Environment. 2020;715:136671. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136671. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexandra, M., Helene, O., Jiri, M., & Maria, V. (2020). The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review sources. Science of the Environment, 709. 10.1016/j.scitotenv - PubMed
-
- Ali H, Khan E. What are heavy metals? The long-standing controversy over the scientific use of the term ‘heavy metals’-proposal of a comprehensive definition. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry. 2018;100:6–19. doi: 10.1080/02772248.2017.1413652. - DOI
-
- Al-Saydeh SA, El-Naas MH, Zaidi SJ. Copper removal from industrial wastewater: a comprehensive review. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 2017;56:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.07.026. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

