Isradipine therapy in Cacna1dIle772Met/+ mice ameliorates primary aldosteronism and neurologic abnormalities
- PMID: 37698934
- PMCID: PMC10619505
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.162468
Isradipine therapy in Cacna1dIle772Met/+ mice ameliorates primary aldosteronism and neurologic abnormalities
Abstract
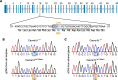
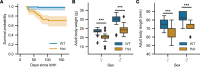
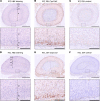
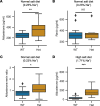
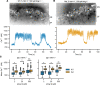
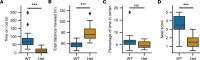
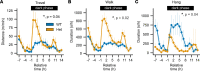
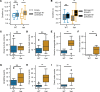
Somatic gain-of-function mutations in the L-type calcium channel CaV1.3 (CACNA1D gene) cause adrenal aldosterone-producing adenomas and micronodules. De novo germline mutations are found in a syndrome of primary aldosteronism, seizures, and neurologic abnormalities (PASNA) as well as in autism spectrum disorder. Using CRISPR/Cas9, we here generated mice with a Cacna1d gain-of-function mutation found in both adenomas and PASNA syndrome (Cacna1dIle772Met/+). These mice show reduced body weight and increased mortality from weaning to approximately 100 days of age. Male mice do not breed, likely due to neuromotor impairment, and the offspring of female mice die perinatally, likely due to lack of maternal care. Mice generated by in vitro fertilization showed elevated intracellular calcium in the aldosterone-producing zona glomerulosa, an elevated aldosterone/renin ratio, and persistently elevated serum aldosterone on a high-salt diet as signs of primary aldosteronism. Anesthesia with ketamine and xylazine induced tonic-clonic seizures. Neurologic abnormalities included hyperlocomotion, impaired performance in the rotarod test, impaired nest building, and slight changes in social behavior. Intracellular calcium in the zona glomerulosa, aldosterone levels, and rotarod performance responded to treatment with the calcium channel blocker isradipine, with implications for the therapy of patients with aldosterone-producing lesions and with PASNA syndrome.
Keywords: Endocrinology; Hypertension; Mouse models; Neurological disorders; Neuroscience.
Figures
References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398(10304):957–980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

