Diagnostic accuracy of Ascertain Dementia 8-item Questionnaire by participant and informant-A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37699028
- PMCID: PMC10497164
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291291
Diagnostic accuracy of Ascertain Dementia 8-item Questionnaire by participant and informant-A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The Ascertain Dementia 8-item Questionnaire (AD8) is a screening tool for cognitive impairment that can be administered to older persons and/or their informants.
Objectives: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy and compare the predictive parameters of the informant and participant-completed Ascertain Dementia 8-item Questionnaire (iAD8 and pAD8, respectively) in older adults with cognitive impairment.
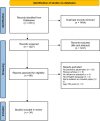
Methods/design: We searched ten electronic databases (including MEDLINE (Ovid), Embase) from tool inception to March 2022. We included studies with patients ≥60 years old that were screened for cognitive impairment using AD8 in any healthcare setting. Predictive parameters were assessed against reference standards to estimate accuracy and diagnostic ability using bivariate random-effects meta-analyses. We used QUADAS-2 criteria to assess risk of bias.
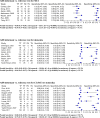
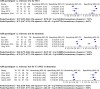
Results: A cut-off of ≥2/8 was used to classify mild cognitive impairment (MCI), dementia, and cognitive impairment (MCI or dementia). Seven studies using the iAD8 (n = 794) showed a sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 79% to detect MCI. Nine studies using the iAD8 (n = 2393) established 91% sensitivity and 64% specificity to detect dementia. To detect MCI using the pAD8, four studies (n = 836) showed 57% sensitivity and 71% specificity. To detect dementia using the pAD8, four studies (n = 3015) demonstrated 82% sensitivity and 75% specificity. Recurring high or unclear risk of bias was noted in the domains of "Index test" and "reference standard".
Conclusions: The diagnostic accuracy of iAD8 is superior to that of pAD8 when screening for cognitive impairment. The AD8 may be an acceptable alternative to screen for cognitive impairment in older adults when there are limitations to formal testing.
Copyright: © 2023 Tanwani et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests. Frances Chung reports research support from the Ontario Ministry of Health Innovation Grant, ResMed Foundation, University Health Network Foundation, Consultant to Takeda, and STOP-Bang Questionnaire proprietary to University Health Network. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Gauthier S, Rosa-Neto P, Morais JA, Webster C. World Alzheimer Report 2021: Journey through the diagnosis of dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International. 2021.
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on the public health response to dementia. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2021.
-
- Molnar F, Frank C. Cognitive screening of older patients. Canadian Family Physician. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

