Amino acid metabolism in health and disease
- PMID: 37699892
- PMCID: PMC10497558
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01569-3
Amino acid metabolism in health and disease
Abstract
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein synthesis. They are structural elements and energy sources of cells necessary for normal cell growth, differentiation and function. Amino acid metabolism disorders have been linked with a number of pathological conditions, including metabolic diseases, cardiovascular diseases, immune diseases, and cancer. In the case of tumors, alterations in amino acid metabolism can be used not only as clinical indicators of cancer progression but also as therapeutic strategies. Since the growth and development of tumors depend on the intake of foreign amino acids, more and more studies have targeted the metabolism of tumor-related amino acids to selectively kill tumor cells. Furthermore, immune-related studies have confirmed that amino acid metabolism regulates the function of effector T cells and regulatory T cells, affecting the function of immune cells. Therefore, studying amino acid metabolism associated with disease and identifying targets in amino acid metabolic pathways may be helpful for disease treatment. This article mainly focuses on the research of amino acid metabolism in tumor-oriented diseases, and reviews the research and clinical research progress of metabolic diseases, cardiovascular diseases and immune-related diseases related to amino acid metabolism, in order to provide theoretical basis for targeted therapy of amino acid metabolism.
© 2023. West China Hospital, Sichuan University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
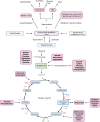
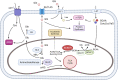
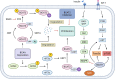

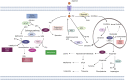



References
-
- Horton, H. R. et al. (eds) Principles of Biochemistry (Pearson Press, 2006).
-
- Latham, M. C. (ed) Human Nutrition in the Developing World (Food & Agriculture Org. Press, 1997).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

