TIMP-1 Protects Tight Junctions of Brain Endothelial Cells From MMP-Mediated Degradation
- PMID: 37700105
- PMCID: PMC10878538
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-023-03593-y
TIMP-1 Protects Tight Junctions of Brain Endothelial Cells From MMP-Mediated Degradation
Abstract
Objective: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) plays a critical role in central nervous system homeostasis, and the integrity of BBB is disrupted in many neurodegenerative diseases. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) degrade the tight junctions (TJs) of endothelial cells and basement membrane components essential to BBB integrity, which leads to increased BBB permeability and allows inflammatory cells and neurotoxic substances to enter the brain. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), endogenous inhibitors of MMPs, regulate MMP activity, thereby maintaining BBB integrity.
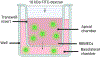
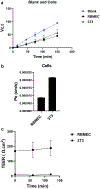
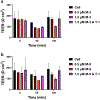
Methods: The disruptive impacts of MMP-3 and MMP-9 on BBB and protective effect of TIMP-1 were investigated in a simplified in vitro model of the BBB, which was generated using rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (RBMEC). The main features of BBB formation, including permeability and the trans-endothelial electrical resistance (TEER), were monitored over time after the addition of MMP-3 and MMP-9 and their complexes with TIMP-1 inhibitor.
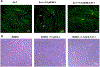
Results: Our results indicated that MMP-3 and MMP-9 caused a dose-dependent disruption of the BBB, with 1.5 µM MMPs resulting in an over threefold increase in permeability, while TIMP-1 inhibition protected the integrity of the BBB model and recovered TEER and permeability of RBMECs. The disruption and recovery of tight junction proteins of RBMECs after MMP and TIMP treatment were also detected using fluorescent microscopy.
Conclusion: MMP-9 and MMP-3 disrupt the BBB by degrading tight junctions in endothelial cells, and TIMP-1 could inhibit the disruptive effect of MMP-3 and MMP-9 by showing potential as therapeutic protein against MMP-related diseases where BBB disruption plays a role.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier (BBB); drug delivery; matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs); neurodegenerative diseases; tissue Inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Loss of flow induces leukocyte-mediated MMP/TIMP imbalance in dynamic in vitro blood-brain barrier model: role of pro-inflammatory cytokines.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Oct;291(4):C740-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00516.2005. Epub 2006 May 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16707552
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secreted by leukemic cells increase the permeability of blood-brain barrier by disrupting tight junction proteins.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e20599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020599. Epub 2011 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21857898 Free PMC article.
-
West Nile virus-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier in mice is characterized by the degradation of the junctional complex proteins and increase in multiple matrix metalloproteinases.J Gen Virol. 2012 Jun;93(Pt 6):1193-1203. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.040899-0. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22398316 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier abnormalities caused by HIV-1 gp120: mechanistic and therapeutic implications.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:482575. doi: 10.1100/2012/482575. Epub 2012 Feb 1. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22448134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of free radicals, matrix metalloproteinases and caveolin-1 impacts blood-brain barrier permeability.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011 Jun 1;3(4):1216-31. doi: 10.2741/222. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011. PMID: 21622267 Review.
Cited by
-
Blood-brain barrier disruption: a culprit of cognitive decline?Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Aug 7;21(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00563-3. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 39113115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Different Doses of Glucosamine Hydrochloride on Cartilage Tissue and Levels of Joint Injury Markers in Knee Osteoarthritis.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 May;29(10):e70579. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70579. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40387631 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of TIMPs and their minimally engineered variants in blocking invasion and migration of brain cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2025 Feb 28;16:118-130. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28691. Oncotarget. 2025. PMID: 40019229 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Dynamics and Microbiome Crosstalk: Matrix Metalloproteinases as Key Players in Disease and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 11;26(8):3621. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083621. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal MicroRNA: an Effective Strategy for the Treatment of Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):9966-9979. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04886-6. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40175714 Review.
References
-
- Asahi M, Wang X, Mori T, Sumii T, Jung JC, Moskowitz MA, et al. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on the proteolysis of blood-brain barrier and white matter components after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 2001;21(19):7724–32. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-19-07724.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

