Value of biplane transrectal ultrasonography plus micro-flow imaging in preoperative T staging and rectal cancer diagnosis in combination with CEA/CA199 and MRI
- PMID: 37700269
- PMCID: PMC10496222
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-11370-8
Value of biplane transrectal ultrasonography plus micro-flow imaging in preoperative T staging and rectal cancer diagnosis in combination with CEA/CA199 and MRI
Abstract
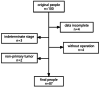
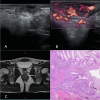
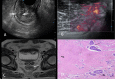
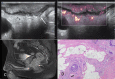
Background: Rectal cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors and has a high incidence rate and fatality rate. Accurate preoperative T staging of rectal cancer is critical for the selection of appropriate rectal cancer treatment. Various pre-operative imaging methods are available, and the identification of the most accurate method for clinical use is essential for patient care. We investigated the value of biplane transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) combined with MFI in preoperative staging of rectal cancer and explored the value of combining TRUS plus MFI with CEA/CA199 and MRI.
Methods: A total of 87 patients from Daping Hospital with rectal cancer who underwent TRUS examination plus MFI were included. Grades of MFI were determined by Alder classification. Among the total patients, 64 underwent MRI and serum CEA/CA199 tests additionally within one week of TRUS. Pathological results were used as the gold standard for cancer staging. Concordance rates between TRUS, MRI, and CEA/CA199 for tumors at different stages were compared.
Results: There were no significant differences between the Alder classification and pathological T staging. The concordance rate of TRUS and MFI for rectal cancer T staging was 72.4% (K = 0.615, p < 0.001). Serum CEA and CA199 levels were significantly different in tumors at different stages and increased progressively by pathological stage (p < 0.001); the accuracy rate was 71.88% (K = 0.599, p < 0.001), while that of MRI was 51.56% (K = 0.303, p < 0.001), indicating that TRUS had higher consistency in the preoperative T staging of rectal cancer. The combination of TRUS, MRI, and CEA/CA199 yielded an accuracy rate of 90.6%, which was higher than that of any method alone.
Conclusions: Preoperative T staging of rectal cancer from biplane TRUS plus MFI was highly consistent with postoperative pathological T staging. TRUS combined with MRI and serum CEA/CA199 had a greater value in the diagnosis of rectal cancer and a higher diagnostic rate than any examination alone.
Keywords: Biplane TRUS; CA199; CEA; Combined; MFI; MRI; Rectal Cancer; Tumor staging.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Application value of biplane transrectal ultrasonography plus ultrasonic elastosonography and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in preoperative T staging after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer.Eur J Radiol. 2018 Jul;104:20-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.04.027. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29857861
-
Biplane transrectal ultrasonography plus ultrasonic elastosonography and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in T staging of rectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Sep 7;20(1):862. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07369-0. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32894078 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Value of the Combined Detection of Enhanced CT, MRI, CEA, and CA199 in the Diagnosis of Rectal Cancer.J Oncol. 2021 Jul 13;2021:8585371. doi: 10.1155/2021/8585371. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34335762 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI in detection and staging of prostate cancer.Dan Med J. 2017 Feb;64(2):B5327. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28157066 Review.
-
[Staging and Diagnostics of Rectal Cancer].Zentralbl Chir. 2024 Feb;149(1):37-45. doi: 10.1055/a-2252-2320. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Zentralbl Chir. 2024. PMID: 38442882 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Update on newer ultrasound systems to study the microvasculature.Radiol Med. 2025 Aug;130(8):1283-1296. doi: 10.1007/s11547-025-02035-6. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Radiol Med. 2025. PMID: 40560337 Review.
-
The role of preoperative FPR and FAR in prognostic evaluation of stages II and III radical colorectal cancer: A single-center retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 17;103(20):e38145. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038145. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38758911 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion and T-staging of rectal cancer via a dual-energy computed tomography iodine map: a feasibility study.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025 Jan 1;31(1):1-9. doi: 10.4274/dir.2024.242755. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025. PMID: 38836502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A, Cancer Statistics. 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Erratum in: CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(4):359. PMID: 33433946. - PubMed
-
- Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Cederquist L, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, Cohen S, Cooper HS, Deming D, Engstrom PF, Grem JL, Grothey A, Hochster HS, Hoffe S, Hunt S, Kamel A, Kirilcuk N, Krishnamurthi S, Messersmith WA, Meyerhardt J, Mulcahy MF, Murphy JD, Nurkin S, Saltz L, Sharma S, Shibata D, Skibber JM, Sofocleous CT, Stoffel EM, Stotsky-Himelfarb E, Willett CG, Wuthrick E, Gregory KM, Gurski L, Freedman-Cass DA. Rectal Cancer, Version 2.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16(7):874–901. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- cstc2018jscx-msybX0018/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- cstc2018jscx-msybX0018/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- cstc2018jscx-msybX0018/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- cstc2018jscx-msybX0018/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- cstc2018jscx-msybX0018/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

