A New and Effective Technique in the Endoscopic Treatment of Obesity and Regulation of Diabetes: The Pyloric Revision
- PMID: 37701000
- PMCID: PMC10493824
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43357
A New and Effective Technique in the Endoscopic Treatment of Obesity and Regulation of Diabetes: The Pyloric Revision
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the role of the functional structure of the pylorus in obesity and diabetes and to determine the efficacy of a new method, pyloric revision (PR), in the treatment.
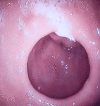
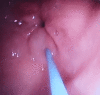
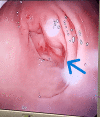
Methods: The pyloric structures of the patients who applied for endoscopic obesity treatment were examined, and the patients were classified as normotonic (NP), hypotonic (HP), and atonic (AP) according to their pyloric structures. PR was applied to those with pyloric structural disorders. Patients with NP were also given the preferred endoscopic treatment (balloon, botulinum toxin, Kanlioz technique). In addition, the pre-procedure fasting blood glucose (FBG) and glycated hemoglobin levels (HbA1c) of the patients were compared with the sixth-month post-procedure status. In order to compare the pyloric structure and other parameters in normal weights with the obese group, a second group of 100 normal-weight (BMI<25) individuals was formed and compared with the study group.
Results: In patients with HP (93 patients) and AP (61 patients), a statistically significant decrease was found between HbA1c and FBG levels before treatment and six months after treatment (p˂0.02, p<0.001, respectively). There was a statistically significant difference in favor of the endoscopic obesity treatment group (EOTG) in terms of pyloric disorder, HbA1c, and FPG levels between the EOTG and the normal weight group (NWG) (p<0.0001).
Conclusion: We recommend using PR as an easy-to-perform, effective, minimally invasive, reproducible, and cost-effective technique that does not require hospitalization.
Keywords: appetite and sateity; diabetes mellitus; endoscopic obesity treatments; feeling of fullness; obesity treatment; pyloric revision.
Copyright © 2023, Kanlioz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How Taking into Account the Pyloric Tonus Contributes to Treatment Success While Administering Gastric "Botulinum Toxin A" for Weight Loss.Obes Surg. 2020 Sep;30(9):3365-3369. doi: 10.1007/s11695-020-04556-7. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 32405906
-
Endoscopic management of obesity: Impact of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty on weight loss and co-morbidities at six months and one year.J Visc Surg. 2023 Apr;160(2S):S38-S46. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2022.12.003. Epub 2023 Jan 30. J Visc Surg. 2023. PMID: 36725451 Review.
-
Gastric electrical stimulation: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(16):1-79. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074486 Free PMC article.
-
Pyloric sphincter characteristics using EndoFLIP® in gastroparesis.Rev Gastroenterol Mex (Engl Ed). 2018 Oct-Dec;83(4):375-384. doi: 10.1016/j.rgmx.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Rev Gastroenterol Mex (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 29709494 English, Spanish.
-
Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy versus pyloric injection of botulinum toxin for the treatment of gastroparesis: our institutional experience and a systematic review of the literature.Surg Endosc. 2023 Sep;37(9):7280-7287. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10262-z. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37430121
References
-
- Obesity: basic considerations and clinical approaches. Bray GA. Dis Mon. 1989;35:449–537. - PubMed
-
- The spread of the obesity epidemic in the United States, 1991-1998. Mokdad AH, Serdula MK, Dietz WH, Bowman BA, Marks JS, Koplan JP. JAMA. 1999;282:1519–1522. - PubMed
-
- Sedentarism, active lifestyle and sport: Impact on health and obesity prevention. González-Gross M, Meléndez A. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28 Suppl 5:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Association of sports and physical activity with obesity among teenagers in Poland. Glinkowska B, Glinkowski WM. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2018;31:771–782. - PubMed
-
- Quality of life and obesity. Kolotkin RL, Meter K, Williams GR. Obes Rev. 2001;2:219–229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous