Epidemiology of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Trauma Patients Admitted to a Trauma Center in Northern India: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 37701009
- PMCID: PMC10493041
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43327
Epidemiology of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Trauma Patients Admitted to a Trauma Center in Northern India: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
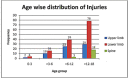
Background Pediatric injuries are the leading cause of death and disability worldwide and place a considerable burden on nations with limited resources. A careful investigation of the epidemiology of pediatric musculoskeletal trauma can provide insight into its causation and the demography of the affected children and help us devise preventive strategies to reduce the burden of pediatric musculoskeletal trauma. Methodology Musculoskeletal trauma patients up to the age of 18 years were included in this prospective cohort study. Information about age, sex, time since the injury to presentation to a trauma center, mode of injury, the site where the injury was suffered, and the exact injury were recorded. Age was further recorded as 0 to 3 years, >3 to 6 years, >6 to 12 years, and >12 to 18 years. A subgroup analysis of the mode of injury was done using age group and sex. Results A total of 201 patients were enrolled in the study. The age (mean ± standard deviation [SD]) of the enrolled patients was 12.48 ± 4.71 years. Of the 201 patients enrolled, 146 (72.63%) were males. The mean time since the injury to the reception in the emergency department of the King George's Medical University trauma center (a tertiary care center) was 19.13 ± 33.86 hours. The common mechanisms of injury observed were road traffic accidents (RTAs, 55.22%), falls from height (29.35%), and falls at ground level. There was a significant difference in the mode of injury in the age groups (P = 0.0297) and among males and females (P = 0.0034). Injuries to the lower limbs were most common in all age groups. Conclusions Our study presents the baseline epidemiological data on pediatric musculoskeletal injuries distributed by age groups, gender, mode of injury, site of injury, and region-wise distribution of injuries. The data may be used by policymakers in planning a pediatric trauma care system in India.
Keywords: epidemiology; fracture; injury; musculoskeletal; pediatric trauma.
Copyright © 2023, Verma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Trauma Patients Admitted to the Trauma Center of King George's Medical University (KGMU) During COVID-19-Induced Lockdown.Cureus. 2022 Mar 30;14(3):e23648. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23648. eCollection 2022 Mar. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35505752 Free PMC article.
-
Are falls more common than road traffic accidents in pediatric trauma? Experience from a Level 1 trauma centre in New Delhi, India.Chin J Traumatol. 2016 Apr 1;19(2):75-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2015.10.004. Chin J Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 27140213 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern and epidemiology of pediatric musculoskeletal injuries in Kashmir valley, a retrospective single-center study of 1467 patients.J Pediatr Orthop B. 2015 May;24(3):230-7. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000146. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2015. PMID: 25647562
-
Cervical spine injuries in children: a review of 103 patients treated consecutively at a level 1 pediatric trauma center.J Pediatr Surg. 2001 Aug;36(8):1107-14. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2001.25665. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. PMID: 11479837 Review.
-
Traumatic brain injury in Indian children.Childs Nerv Syst. 2018 Jun;34(6):1119-1123. doi: 10.1007/s00381-018-3784-z. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018. PMID: 29594463 Review.
References
-
- WHO/UNICEF WHO/UNICEF. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2005. Child and Adolescent Injury Prevention: A Global Call to Action.
-
- World report on child injury prevention appeals to "Keep Kids Safe". Peden M. Inj Prev. 2008;14:413–414. - PubMed
-
- Holder Y, Peden M, Krug E, Lund J, Gururaj G, Kobusingye O. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2001. Injury Survelliance Guidelines.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources