Impact of Ovarian Factor Mediums on the Apoptotic Gene Expression and Embryo Quality Derived From Vitrified Immature Human Oocytes
- PMID: 37701087
- PMCID: PMC10492718
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-022-01726-8
Impact of Ovarian Factor Mediums on the Apoptotic Gene Expression and Embryo Quality Derived From Vitrified Immature Human Oocytes
Abstract
Background: Condition mediums have a potential role in oocyte development. In this study, we evaluated the effects of different mediums on the developmental potential of vitrified immature human oocyte after IVM and parthenogenesis by ionomycin.
Methods: Immature oocytes were collected from 184 women after vitrification/thawing and maturation, in three types of IVM mediums separately. Finally, 151 IVM MΙΙ oocytes were obtained and randomly divided into six groups and underwent the following intervention. Fresh and vitrified-thawing MΙΙ oocytes were activated after IVM in three conditioned mediums by ionomycin. Mediums included 1) Minimum Essential Medium Alpha (α-MEM) (as control medium), 2) α-MEM supplemented with supernatants of Mesenchyme bone marrow (B.M), 3) α-MEM with ovarian growth factors (O.F). Then, scoring of parthenote embryos was undertaken in accordance with pertinent morphological properties. Moreover, the expression of Bax and Bcl2 were determined in the parthenote embryos.
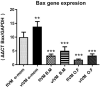
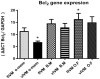
Result: Percentage of the degenerated oocyte, 2-4 cells, 4-8 cells, and 16 cells, was different in the experimental groups. Also, cytoplasmic maturation and blastocyst formation rates were significantly different (p < 0.05) between the control and the other mediums. The highest mRNA expression levels of Bcl2 and Bax genes in parthenotes were observed in the fIVM O.F and vIVM α-MEM mediums, respectively. vIVM, α-MEM and fIVM O.F showed the lowest expression of Bcl2 and Bax genes, respectively.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that the O.F. medium had more potent effects on oocyte growth and cytoplasmic maturation up to the blastocyst stage with the highest expression level of the BCL2 gene and the lowest relative amount of the BAX gene in this medium. The results of the present study have been verified only for parthenogenetically activated embryos, and any positive effect of the environment on the egg/embryo fertilized with sperm requires more extensive studies.
Keywords: Conditioned medium; Developmental potential; IVM; Oocyte activation; Parthenogenesis.
© Federation of Obstetric & Gynecological Societies of India 2022. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akbari H, Vaghefi SHE, Shahedi A, et al. Conditioned mediums and human oocytes in vitro maturation. Int J Pharm Phytopharm Res (eIJPPR) 2018;8(2):64–71.
-
- Akbari H. The effect of conditioned media on mouse oocytes ultrastructure following in vitro maturation. Gene Reports. 2020;20:100732. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100732. - DOI
-
- Akbari H, Vaghefi SHE, Shahedi A, et al. The effect of conditioned media on human oocyte maturation and developmental competence. Pharmacophore. 2017;8(6s):e1173457.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials