Induction of metallothionein expression by supplementation of zinc induces resistance against platinum-based treatment in malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 37701096
- PMCID: PMC10493783
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-2651
Induction of metallothionein expression by supplementation of zinc induces resistance against platinum-based treatment in malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
Background: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive tumor with a dismal prognosis. Currently, multimodality treatment including chemotherapy with cisplatin or carboplatin in combination with pemetrexed offers the best options. Detoxification of heavy metals in the cell by metallothioneins (MT) is associated with early failure to platin-based chemotherapy. The induction of MTs gene expression or its enzyme results in saturation by exposure to metal ions such as zinc or cadmium. Its therapeutically effect is still not analyzed in depth.
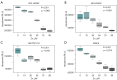
Methods: In our study, we investigated three MPM cell lines and one fibroblast cell line in the course of cisplatin treatment and supplementation of zinc. Cell state analyses via an enzyme-activity based assay were performed. With this, we were able to analyze apoptosis, necrosis and viability of cells. Additionally, we tested treated cells for changes in metallothionein IIA (MT2A) expression by using quantitative realtime polymerase chain reaction.
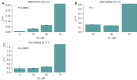
Results: Zinc supplementation induces gene expression of MT2A. Overall, a zinc dose-dependent induction of apoptosis under platin-based treatment could be observed. This effect could be verified in all analyzed cell lines in varying intensity.
Conclusions: MT expression is induced by zinc in a dose-dependent manner and inhibits a successful cisplatin therapy. Therefore, heavy metal exposure during cisplatin therapy, e.g., via cigarette smoke, might be an important factor. This should be considered in further therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM); cisplatin; metallothionein; zinc.
2023 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-2651/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of metallothionein-knockdown on cisplatin resistance in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 29;10(1):18677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75807-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33122816 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemically detectable metallothionein expression in malignant pleural mesotheliomas is strongly associated with early failure to platin-based chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 27;9(32):22254-22268. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24962. eCollection 2018 Apr 27. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29854276 Free PMC article.
-
JQ1, a BET Inhibitor, Synergizes with Cisplatin and Induces Apoptosis in Highly Chemoresistant Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(8):816-828. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666170623101722. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28669341
-
Malignant pleural mesothelioma.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2012 Mar 1;69(5):377-85. doi: 10.2146/ajhp110281. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22345416 Review.
-
Patterns of failure following surgical resection for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Thorac Surg Clin. 2004 Nov;14(4):567-73. doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2004.06.006. Thorac Surg Clin. 2004. PMID: 15559064 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc and its binding proteins: essential roles and therapeutic potential.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jan;99(1):23-41. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03891-3. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39508885 Review.
References
-
- Boons CC, VAN Tulder MW, Burgers JA, et al. The value of pemetrexed for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: a comprehensive review. Anticancer Res 2013;33:3553-61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
